Hop Picking Photographs

Book now for my tours through August, September & October
This selection of hop picking photographs is from the archive of Tower Hamlets Community Housing. Traditionally, this was the time when East Enders headed down to the Hop Farms of Kent & Sussex, embracing the opportunity of a breath of country air and earning a few bob too.
Bill Brownlow, Margie Brownlow, Terry Brownlow & Kate Milchard, with Keith Brownlow & Kevin Locke in front, at Guinness’ Northland’s Farm at Bodiam, Sussex, in 1958. Guinness bought land at Bodiam in 1905 and eight hundred acres were devoted to hop growing at its peak.
Julie Mason, Ted Hart, Edward Hart & friends at Hoathleys Farm, Hook Green, near Lamberhurst, Kent
Lou Osbourn, Derek Protheroe & Kate Day at Goudhurst Farm
Margie Brownlow & Charlie Brownlow with Keith Brownlow, Kate Milchard & Terry Brownlow in front at Guinness’ Northland’s Farm at Bodiam, Sussex, in 1950
Mr & Mrs Gallagher with Kitty Adams & Jackie Gallagher from Westport St, Stepney, in the hop gardens at Pembles Farm, Five Oak Green, Kent in 1959
Jackie Harrop, Joan Day & George Rogers at Whitbread’s Farm, Beltring, Kent in 1949
Mag Day (on the left at the back) in the hop gardens with others at Highwood’s Farm, Collier St, in 1938
Pop Harrop at Whitbread’s Farm, Beltring, Kent in 1949
Sarah Watt, Mrs Hopkins, Steven Allen, Ann Allen, Tom, Albert Allen & Sally Watt in the hop gardens at Jack Thompsett’s Den Farm, Collier St, Kent in 1943
Harry Watt, Tom Shuffle, Mary Shuffle, Sally Watt, Julie Callagher, Ada Watt & Sarah Watt in the hop gardens at Jack Thompsett’s Den Farm, Collier St, Kent in the fifties
Harry Watt, Sally Watt, Sarah Watt holding Terry Ellames in the hop gardens at Jack Thompsett’s Den Farm, Collier St, Kent in 1957
Harry Ayres, a pole puller, in the hop gardens at Diamond Place Farm, Nettlestead, Kent
Emmie Rist, Theresa Webber, Kit Webber & Eileen Ayres in the hop gardens at Diamond Place Farm, Nettlestead, Kent
Kit Webber with her Aunt Mary, her Dad Sam Webber and her Mum, Emmie Ris,t in the hop gardens at Diamond Place Farm, Nettlestead, Kent
Harry Ayres with his wife Kit Webber in the hop gardens at Diamond Place Farm, Nettlestead, Kent.
Richard Pyburn, Mag Day, Patty Seach and Kitty Gray from Kirks Place, Limehouse, in the hop gardens at Highwoods Farm, Collier St, Kent
The Gorst and Webber families at Jack Thompsett’s Farm, Fowle Hall, Kent in the forties
Kitty Waters with sons Terry & John outside the huts at Pembles Farm, Five Oak Green, Kent in 1952
Mr & Mrs Gallagher from Westport St, Stepney, with their grandchildren in the hop gardens at Pembles Farm, Five Oak Green, Kent in 1958
Sybil Ogden, Doris Cossey, Danny Tyrrell & Sally Hawes near Yalding, Kent
John Doree, Alice Thomas, Celia Doree & Mavis Doree in the hop gardens near Cranbrook, Kent
Bill Thomas & his wife Annie, in the hop gardens near Cranbrook, Kent
The Castleman Family from Poplar hop picking in the twenties
Terry & Margie Brownlow at Guinness’ Northland’s Farm at Bodiam in Sussex in 1949
Alfie Raines, Johnny Raines, Charlie Cushway, Les Benjamin & Tommy Webber in the Hop Gardens at Jack Thompsett’s Farm at Fowl Hall near Paddock Wood in Kent
Lal Outram, Wag Outram & Mary Day on the common at Jack Thompsett’s Farm at Fowl Hall near Paddock Wood in Kent in 1955
Taken in September 1958 at Moat Farm, Five Oak Green, Kent. Sitting on the bin is Miss Whitby with Patrick Mahoney, young John Mahoney and Sheila Tarling (now Mahoney) – Sheila & Patrick were picking to save up for their engagement party in October
Maryann Lowry’s Nan, Maggie ,on the left with her Great-Grandmother, Maryann, in the check shirt in the hop gardens, c.1910
Having a rest in hop gardens at Whitbread’s Farm, Beltring, Kent in 1966. In the back row are Mary Brownlow, Sean Locke, Linda Locke, Kate Milchard, Chris Locke & Margie Brownlow with Kevin Locke and Terry Locke in front.
Margie Brownlow & her Mum Kate Milchard at Whitbreads Farm in Beltring, Kent in 1967. These huts were two stories high. The children playing outside are – Timmy Kaylor, Chrissy Locke, Terry Locke, Sean Locke, Linda Locke & Kevin Locke.
Chris Locke, Sally Brownlow, Linda Brownlow, Kate Milchard, Margie Brownlow, Terry Locke & Mary Brownlow at Whitbread’s Farm, Beltring, Kent in 1962
Johnno Mahoney, Superintendant of the Caretakers on the Bancroft Estate in Stepney, driving the “Mahoney Special” at Five Oak Green in 1947
The Clarkson family in the hop gardens in Staplehurst. Gladys Clarkson , Edith Clarkson, William Clarkson, Rose Clarkson & Henry Norris.
John Moore, Ross, Janet Ambler, Maureen Irish & Dennis Mortimer in 1950 at Luck’s Farm, East Peckham, Kent
Kate Fairclough, Mrs Callaghan, Mary Fairclough & Iris Fairclough at Moat Farm, Five Oak Green, Kent in 1972
A gang of Hoppers from Wapping outside the brick huts at Stilstead Farm, Tonbridge, Kent with Jim Tuck & John James in the back. In the middle row the first person on the left is unknown, but the others are Rose Tuck, holding Terry Tuck, Rose Tuck, Danny Tuck & Nell Jenkins. In the front are Alan Jenkins, Brian Tuck, Pat Tuck, Jean Tuck, Terry Taylor & Brian Taylor.
Nanny Barnes, Harriet Hefflin, “Minie” Mahoney & Patsy Mahoney at Ploggs Hall Farm
In the Hop Gardens at Jack Thompsett’s Farm at Fowl Hall, near Paddock Wood in Kent in the late forties. Alfie Raines, Edie Cooper, Margie Gorst & Lizzie Raines
The Day family from Kirks Place, Limehouse, at Highwoods Farm in Collier St, Kent in the fifties
Annie Smith, Bill Daniels, Pearl Brown & Nell Daniels waiting for the measurer in the Hop Garden at Hoathley’s Farm, Hook Green, Kent
On the common outside the huts at at Hoathley’s Farm, Hook Green, Kent – you can see the oasthouses in the distance. Rita Daniels, Colleen Brown, Maureen Brown, Marie Brown, Billy Daniels, Gerald Brown & Teddy Hart , with Sylvie Mason & Pearlie Brown standing.
The Outram family from Arbour Sq outside their huts at Hubbles Farm, Hunton, Kent. Unusually these were detached huts but, like all the others, they made of corrugated tin and all had one small window – simply basic rooms, roughly eleven feet square
Janis Randall being held by her mother Joyce Lee andalongside her is her father, Alfred Lee in a hop garden, near Faversham in September 1950
David & Vivian Lee sitting on a log on the common outside Nissen huts used to house hop pickers
Gerald Brown, Billy Daniels & Dennis Woodham in the hop gardens at Gatehouse Farm near Brenchley, Kent, in the fifties
Nelly Jones from St Paul’s Way with Eileen Mahoney, and in the background is Eileen’s mum, “Minie” Mahoney. Taken in the fifties in the Hop Gardens at Ploggs Hall Farm, between Paddock Wood and Five Oak Green.
At Jack Thompsett’s Farm at Fowl Hall, near Paddock Wood in Kent
Ploggs Hall Farm Ladies Football Team. Back Row – Fred Archer, Lil Callaghan, Harriet Jones, Unknown, Unknown, Nanny Barnes, Liz Weeks, Harriet Hefflin, Johnno Mahoney. Front Row – Doris Hurst Eileen Mahoney & Nellie Jones
John Moore, Ross, Janet Ambler, Maureen Irish & Dennis Mortimer in 1950 at Luck’s Farm, East Peckham, Kent
The Outram and Pyburn families outside a Kent pub in 1957, showing clockwise Kitty Tyrrell, Mary Pyburn, Charlie Protheroe, Rene Protheroe, Wag Outram, Derek Protheroe in the pram, Annie Lazel, Tom Pyburn, Bill Dignum & Nancy Wright.
Sally Watt’s Hop Picker’s account book from Jack Thompsett’s Den Farm, Collier St, Kent in the fifties
You may also like to take a look at
Roy Wild, Hop Picker

Book now for my tours through August, September & October

There is Roy on the far right with his left hand stuck in his pocket, to indicate the appropriate air of nonchalance befitting a street-wise man of the world of around twelve years old, on a hopping expedition with his family from Hoxton.
Roy went hop picking each year with this relations until he reached the age of eighteen and, at this season, he always recalls his days in Kent. Still in touch with many of those who were there with him in the hop fields in the fifties, Roy was more than happy to get out his photographs and settle down with a cup of tea with a drop of whisky in it, and tell me all about it.
“I first went hopping with my family in 1948 when I was ten or eleven. We went to Selling near Faversham in Kent. The fields were owned by Alan Bruce Neame of Shepherd Neame, and he would employ people to pick the hops which he sold to breweries. We all lined up on the last day and he would pay each of us in person.
Some Londoners went by train from London Bridge St, all waiting on the station and carrying all their stuff with them. We were very fortunate, dad’s brother Ernie, he had an asphalt company and had an open backed lorry, for which he made a frame for a rain canopy, and we all went down to hopping together – our family, Ernie’s family, also Renee’s sister Mary and her family. Ernie would drive down to Hoxton and pick us up at Northport St, with all our bits and pieces, our bags and suitcases with bed linen and that type of thing, and away we’d all go down to Faversham. We’d go at the weekend, so we could spend a day unpacking and be ready to start picking on Monday.
There was us hop pickers from London but Neame would also employ ‘home-dwellers,’ these were Kentish people. The accommodation they lived in was far superior to what we were subjected to. We were given no more than Nissen huts, square huts made of corrugated iron with a door and that was about all, no windows. It was very, very primitive. We washed in a bowl of water and the toilet was a hole dug in a field. My mother would take old palliasses down with us from Hoxton and they would be stuffed with straw or hay from the barn, and that would our mattresses. The beds were made of planks, very basic and supported upon four logs to prop them up off the floor. You’d put the palliasses on top of the planks and the blankets on top of that. The huts were always running alive with creepy-crawlies, so anyone that had a phobia of that wasn’t really suited to hop picking.
There was another room next to it which was half the size, this was our kitchen. My dad would take down an old primus stove for cooking. It was fuelled by paraffin and the more you pumped it up the fiercer the flame, the quicker the cooking. It was only a small thing that sat on a box. The alternative to that was cooking outside. The farmer would provide bundles of twigs known as ‘faggots,’ to fuel the fire and we would rig up a few bricks with a grill where we’d put the kettle and a frying pan. They’d literally get pot-black in the smoke.
We usually went from three weeks to a month hop picking, sometimes the whole of September, and you could stay on for fruit picking. When we first started, we picked into a big long troughs of sacking hanging down inside a wooden frame. They were replaced by six bushel baskets. The tally man would come round with a cart to collect the six bushel baskets and mark your card with how much you had picked, before carrying the hops away to the oasthouses for drying.
At the time, we were paid one shilling and sixpence a bushel. You’d pick into a bushel basket while you were sitting with it between your legs and when it was full, you’d walk over to the six bushel basket and tip it in. My dad was a fast picker, he’d say ‘Come on Roy, do it a bit quicker!’ All your fingers got stained black by the the hops, we called it ‘hoppy hands.’
If you had children with you, they would mess about. Their parents would be rebuking them and telling them to get picking because the more you picked, the more you earned. Some people could get hold of a bine, pull the leaves off and, in one sweep, take all the hops off into the basket. Other people, to bulk up their baskets would put all kinds of things in there. they would put the bines at the bottom of the six bushel basket and nobody would know, but if you got caught then you was in trouble. My dad showed me how to fill a six bushel basket up to the five bushel level and then put your arms down inside to lift up the hops to the top just before the tally man came round.
The adults were dedicated pickers because you had to buy food all the time and being there could cost more money than you made. There was a little store near us called ‘Clinges’ and further up, just past the graveyard, was another store which was more modern called ‘Blythes’, and next door to that was a pub called the ‘White Swan’ and that was the release for all the hop pickers. They all used to go there on Saturday and Sunday nights and there’d be sing-songs and dancing, before going back to work on Monday morning. It was the only enjoyment you had down there, except – if you didn’t go up to the pub – you’d get all the familes sitting round of a weekend and reminiscing and singing songs, round a big open fire made up of the faggots
We worked from nine o’clock until about four, Monday to Friday. The owner of the hop fields employed guys to work for him who were called ‘Pole Pullers,’ they had big long poles with a sharp knife on the end and when you pulled a bine, if it didn’t come down, you’d call out for a pole puller and with his big long pole he’d cut the top of it and the rest if it would fall down. When it was nearing four o’clock, they’d call out ‘Pull no more bines!’ which was what all the kids were waiting for because by this time they’d all had just about enough. A hop field can be one muddy place and if you’re in among all that with wellingtons on it can get pretty sticky. If it was ready to rain, the pole pullers would also go round and call ‘Pull no more bines.’ Nobody was expected to work outside in the rain. We dreaded the rain but we welcomed the pole pullers when they called out, because that was the day’s work done until the following morning.
We looked forward to going hop picking because it was the chance of an adventure in the country. It was just after the war and we’d had it rough in Hoxton. I was born in 1937 and I’d grown up through the war, and we still had ration books for a long time afterwards. I was a young man in the fabulous fifties and the swinging sixties. In the fifties, we had American music and Elvis Presley, and in the sixties the Beatles and British music. Hop picking was being mechanised, they had invented machines that could do it. So we grew away from it, and young men and young women had better things to do with their time.”

Roy stands in the centre of this family group

Renee Wild and Rosie Wild

Picking into a six bushel basket

Roy’s father Andy Wild rides in the cart with his brother Ernie

Roy’s grandfather Andrew Wild is on the far left of this photo

Roy is on the far right of this group

Roy sits in the left in the front of this picture




Rosie, Mary & Renee


Roy’s father Andy Wild with Roy’s mother Rosie at the washing up and Pearl

Roy’s mother, Rosie Wild


Renee, Mary & Pearl

Roy’s father Andy stands on the left and his Uncle Ernie on the right



Roy

Roy (with Trixie) and Tony sit beside their mother Rosie

Roy’s mother and father with his younger brother Tony

Roy stands on the right of this group of his pals
You may also like to read about
The Lives Of the Spitalfields Nippers

Book now for my tours through August, September & October

This boy is wearing Horace Warner’s hat
I often think of the lives of the Spitalfields Nippers. Around 1900 Photographer and Sunday School Teacher Horace Warner took portraits of children in Quaker St, who were some of the poorest in London at that time. When his personal album of these astonishing photographs came to light ten years ago, we researched the lives of his subjects and published a book of all his portraits accompanied by biographies of the children. Although sold out long ago, secondhand copies of this can be found online.
While we were shocked to discover that as many as a third of these children did not reach adulthood, we were also surprised and heartened by the wide range of outcomes among the others. In spite of the deprivation they endured in their early years, many of these children survived to have long and fulfilled lives.

Walter Seabrook was born on 23rd May 1890 to William and Elizabeth Seabrook of Custance St, Hoxton. In 1901, when Walter’s portrait was taken by Horace Warner, the family were living at 24 & 1/2 Great Pearl St, Spitalfields, and Walter’s father worked as a printer’s labourer. At twenty-four years old, Walter was conscripted and fought in World War One but survived to marry Alice Noon on Christmas Day 1918 at St Matthew’s, Bethnal Green. By occupation, Walter was an electrician and lived at 2 Princes Court, Gibraltar Walk. He and Alice had three children – Walter born in 1919, Alice born in 1922 and Gladys born in 1924. Walter senior died in Ware, Hertfordshire, in 1971, aged eighty-one.

Sisters Wakefield
Jessica & Rosalie Wakefield. Jessica was born in Camden on January 16th 1891 and Rosalie at 47 Hamilton Buildings, Great Eastern St, Shoreditch on July 4th 1895. They were the second and last of four children born to William, a printer’s assistant, and Alice, a housewife. It seems likely they were living in Great Eastern St at the time Horace Warner photographed them, when Jessica was ten or eleven and Rosalie was five or six.
Jessica married Stanley Taylor in 1915 and they lived in Wandsworth, where she died in 1985, aged ninety-four. On July 31st 1918 at the age of twenty-three, Rosalie married Ewart Osborne, a typewriter dealer, who was also twenty-three years old, at St Mary, Balham. After five years of marriage, they had a son named Robert, in 1923, but Ewart left her and she was reported as being deaf. Eventually the couple divorced in 1927 and both married again. Rosalie died aged eighty-four in 1979, six years before her elder sister Jessica, in Waltham Forest.

Jerry Donovan, or ‘Dick Whittington & His Cat’
Jeremiah Donovan was born in 1895 in the City of London. His parents Daniel, news vendor, and Katherine Donovan originated in Ireland. They came to England and settled in Spitalfields at 14 Little Pearl St, Spitalfields. By 1901, the family were resident at Elizabeth Buildings, Boleyn Rd. Jeremiah volunteered for World War I in 1914 when he was nineteen and was stationed at first at City of London Barracks in Moorgate. He joined the Royal Artillery, looked after the horses for the gun carriages, but was gassed in France. In 1919, Jeremiah married Susan Nichols and they had one son, Bertram John Donovan, born in 1920. He died in Dalston in 1956 and is remembered by nine great grandchildren.

Adelaide Springett in all her best clothes
Adelaide Springett was born in February 1893 in the parish of St George-in-the-East, Wapping. Her father, William Springett came from Marylebone and her mother Margaret from St Lukes, Old St. Both parents were costermongers, although William was a dock labourer when he first married. Adelaide’s twin sisters, Ellen and Margaret, died at birth and another sister, Susannah, died aged four. Adelaide attended St Mary’s School and then St Joseph’s School. The addresses on her school admissions were 12 Miller’s Court, Dorset St, and then 26 Dorset St. In 1901, at eight years old, she was recorded as lodging with her mother at the Salvation Army Shelter in Hanbury St.
Adelaide Springett died in 1986 in Fulham aged ninety-three, without any traceable relatives, and the London Borough of Kensington & Chelsea Social Services Department was her executor.

Celia Compton was born in 11 Johnson St, Mile End, on April 28th 1886, to Charles – a wood chopper – and Mary Compton. Celia was one of nine children but only six survived into adulthood. Two elder brothers Charles, born in 1883, and William, born in 1884, both died without reaching their first birthdays, leaving Celia as the eldest. On January 25th 1904, she married George Hayday, a chairmaker who was ten years older than her. They lived at 5 George St, Hoxton, and had no children. After he died in 1933, she married Henry Wood the next year and they lived in George Sq until it was demolished in 1949. In later years, Celia became a moneylender and she died in Poplar in 1966 aged eighty years old.

The Dinners Of Old London

Book now for my tours through August, September & October
Dinner at the Mercers’ Hall, c.1910
Is that your stomach rumbling or is it the sound of distant thunder I hear? To assuage your hunger, let us pass the time until we eat by studying these old glass slides once used for magic lantern shows by the London & Middlesex Archaeological Society at the Bishopsgate Insititute. Observe the architecture of gastronomy as expressed in the number and variety of ancient halls – the dining halls, the banquet halls and the luncheon rooms – where grand people once met for lengthy meals. Let us consider the dinners of old London.
The choicest meat from Smithfield, the finest fish from Billingsgate, and the freshest vegetables from Covent Garden and Spitalfields, they all found their way onto these long tables – such as the one in Middle Temple Hall which is twenty-seven feet long and made of single oak tree donated by Elizabeth I. The trunk was floated down the river from Windsor Great Park and the table was constructed in the hall almost half millennium ago. It has never been moved and through all the intervening centuries – through the Plague and the Fire and the Blitz – it has groaned beneath the weight of the dinners of old London.
Dinners and politics have always been inextricable in London but, whether these meals were a premise to do business, make connections and forge allegiances, or whether these frequent civic gatherings were, in fact, merely the excuse for an endless catalogue of slap-up feasts and beanos, remains open to question. John Keohane, former Chief Yeoman Warder at the Tower of London told me that his troupe acquired their colloquial name of “beefeaters” because – as royal bodyguards – Henry VII granted them the privilege of dining at his table and eating the red meat which was denied to commonfolk. In the medieval world, your place at dinner corresponded literally to your place in society, whether at top table or among the lower orders.
Contemplating all these empty halls where the table has not been laid yet and where rays of sunlight illuminate the particles of dust floating in the silence, I think we may have to wait a while longer before dinner is served in old London.
Christ’s Hospital Hall, c.1910
Buckingham Palace, State Dining Room, c.1910
Grocers’ Hall, c.1910
Ironmongers’ Hall, Court Luncheon Room, c.1910
Mercers’ Livery Hall, 1932
Merchant Taylors’ Hall, c.1910
Painters’ Hall, c.1910
Salters’ Livery Hall, c.1910
Skinners’ Hall, c.1910
Skinners’ Hall, c.1910
Stationers’ Hall, Stock Room, c.1910
Drapers’ Hall, c.1920
The Admiralty Board Room, c.1910
King’s Robing Room, Palace of Westminster, c.1910
Buckingham Palace, Throne Room, c.1910
Houses of Parliament, Robing Room, c.1910
Lincoln’s Inn, Great Hall, c.1910
Lincoln’s Inn Old Hall, c.1928
Drapers’ Hall, c.1920
Middle Temple Hall, c.1910
Mansion House Dining Room, c.1910
Ironmongers’ Hall, Banqueting Room, c.1910
Apothecaries’ Hall, Banquet in the Great Hall, c.1920
Boys preparing to cook, c.1910
Boar’s Head Dinner at Cutler’s Hall, c.1910
Lord Mayor’s Banquet at the Guildhall, 1933
Baddeley Cake & Wine, Drury Lane, c.1930
Glass slides courtesy Bishopsgate Institute
You may also like to take a look at
A Visit To Great Tom At St Paul’s

Book now for my tours through August, September & October

Like bats, bells lead secluded lives hibernating in dark towers high above cathedrals and churches. Thus it was that I set out to climb to the top of the south west tower of St Paul’s Cathedral last week to visit Great Tom, cast by Richard Phelps at the Whitechapel Bell Foundry in 1716.
At 11,474lbs, Great Tom is significantly smaller than Great Paul, its neighbour in the tower at 37,483lbs, yet Great Paul has been silent for many years making Great Tom the largest working bell at St Paul’s and, if Big Ben (30,339lbs) falls silent during renovations this year, then Great Tom will become London’s largest working bell.
To reach Great Tom, I had first to climb the stone staircase beneath the dome of St Paul’s and then walk along inside the roof of the nave. Here, vast brick hemispheres protrude as the reverse of the shallow domes below, creating a strange effect – like a floor of a multi-storey car park for flying saucers. At the west end, a narrow door leads onto the parapet above the front of the cathedral and you descend from the roof of the nave to arrive at the entrance to the south west tower, where a conveniently placed shed serves as a store for spare clock hands.
Inside the stone tower is a hefty wooden structure that supports the clock and the bells above. Here I climbed a metal staircase to take a peek at Great Paul, a sleek grey beast deep in slumber since the mechanism broke years ago. From here, another stone staircase ascends to the open rotunda where expansive views across the city induce stomach-churning awe. I stepped onto a metal bridge within the tower, spying Great Paul below, and raised my eyes to discern the dark outline of Great Tom above me. It was a curious perspective peering up into the darkness of the interior of the ancient bell, since it was also a gaze into time.
When an old bell is recast, any inscriptions are copied onto the new one and an ancient bell like Great Tom may carry a collection of texts which reveal an elaborate history extending back through many centuries. The story of Great Tom begins in Westminster where, from the thirteenth century in the time of Henry III, the large bell in the clocktower of Westminster Palace was known as ‘Great Tom’ or ‘Westminster Tom.’
Great Tom bears an inscription that reads, ‘Tercius aptavit me rex Edwardque vocavit Sancti decore Edwardi signantur ut horae,’ which translates as ‘King Edward III made and named me so that by the grace of St Edward the hours may be marked.’ This inscription is confirmed by John Stowe writing in 1598, ‘He (Edward III) also built to the use of this chapel (though out of the palace court), some distance west, in the little Sanctuary, a strong clochard of stone and timber, covered with lead, and placed therein three great bells, since usually rung at coronations, triumphs, funerals of princes and their obits.’
With the arrival of mechanical clocks, the bell tower in Westminster became redundant and, when it was pulled down in 1698, Great Tom was sold to St Paul’s Cathedral for £385 17s. 6d. Unfortunately, while it was being transported the bell fell off the cart at Temple Bar and cracked. So it was cast by Philip Wightman, adding the inscription ‘MADE BY PHILIP WIGHTMAN 1708. BROUGHT FROM THE RVINES OF WESTMINSTER.’
Yet this recasting was unsatisfactory and the next year Great Tom was cast again by Richard Phelps at the Whitechapel Bell Foundry. This was also unsuccessful and, seven years later, it was was cast yet again by Richard Phelps at Whitechapel, adding the inscription ‘RICHARD PHELPS MADE ME 1716’ and arriving at the fine tone we hear today.
As well as chiming the hours at St Paul’s, Great Tom is also sounded upon the death of royalty and prominent members of the clergy, tolling last for the death of the Queen Mother in 2002. For the sake of my eardrums, I timed my visit to Great Tom between the hours. Once I had climbed down again safely to the ground, I walked around the west front of the cathedral just in time to hear Great Tom strike noontide. Its deep sonorous reverberation contains echoes of all the bells that Great Tom once was, striking the hours and marking out time in London through eight centuries.


Above the nave


Looking west with St Brides in the distance

Spare clock hands

Looking east along the roof of the cathedral

Up to the clock room

The bell frame for Great Paul in the clock room

Great Paul

Looking up to Great Paul

Looking across to the north west tower from the clock room



Looking south to the river

Looking across to the north west tower

Looking down on Great Paul

Looking up into the bell frame

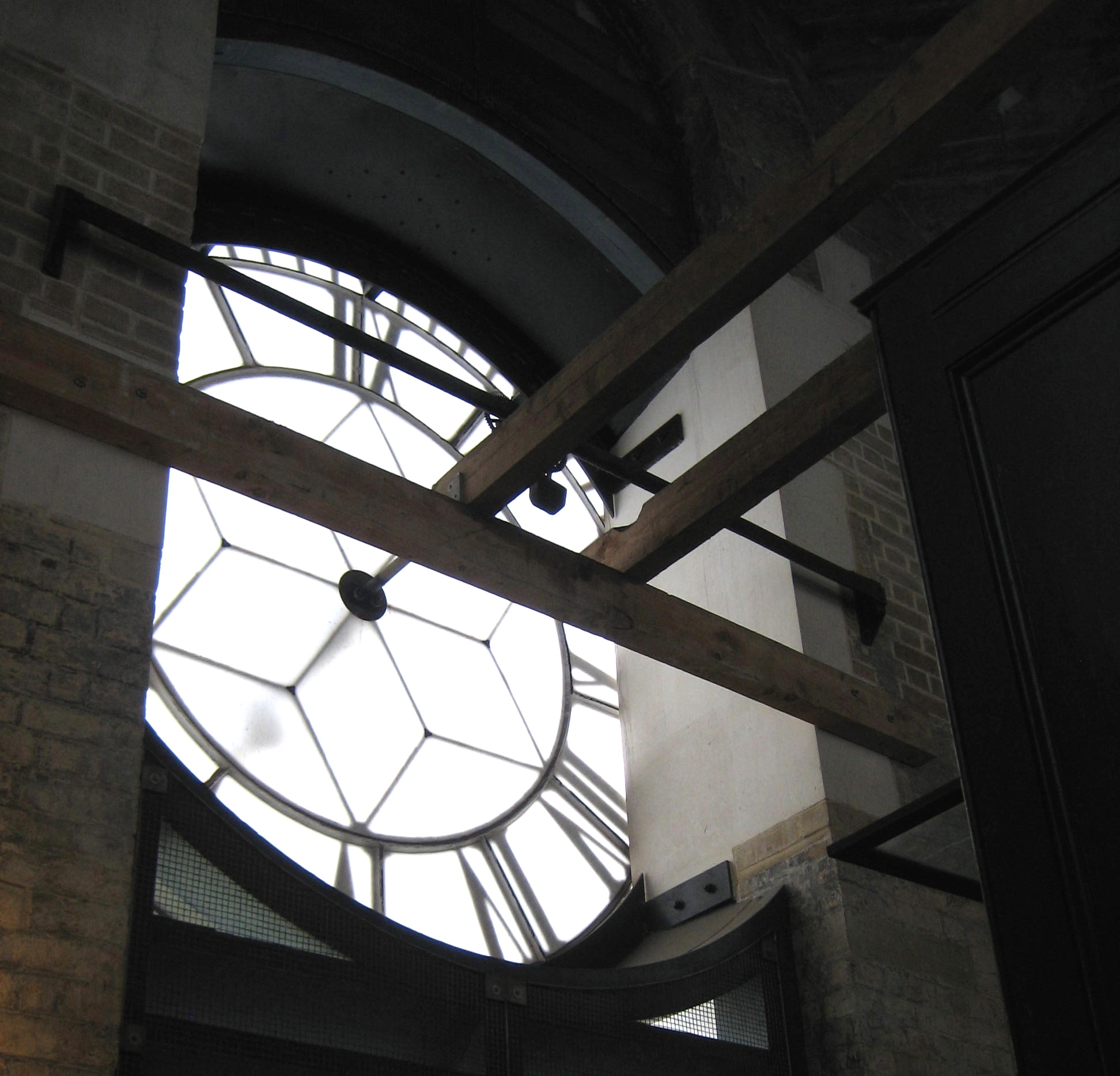
Looking up to catch a glimpse of Great Tom, St Paul’s largest working bell

Great Tom cast by Richard Phelps in Whitechapel in 1716, engraved in 1776 (Courtesy of The Ancient Society of College Youths)

Great Tom strikes noon at St Paul’s Cathedral
You may also like to read about
The Secrets Of Christ Church
Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
There is a such a pleasing geometry to the architecture of Nicholas Hawksmoor’s Christ Church, Spitalfields, completed in 1729, that when you glance upon the satisfying order of the facade you might assume that the internal structure is equally apparent. Yet it is a labyrinth inside. Like a theatre, the building presents a harmonious picture from the centre of the stalls, yet possesses innumerable unseen passages and rooms, backstage.
Beyond the bellringers’ loft, a narrow staircase spirals further into the thickness of the stone spire. As you ascend the worn stone steps within the thickness of the wall, the walls get blacker and the stairs get narrower and the ceiling gets lower. By the time you reach the top, you are stooping as you climb and the giddiness of walking in circles permits the illusion that, as much as you are ascending into the sky, you might equally be descending into the earth. There is a sense that you are beyond the compass of your experience, entering indeterminate space.
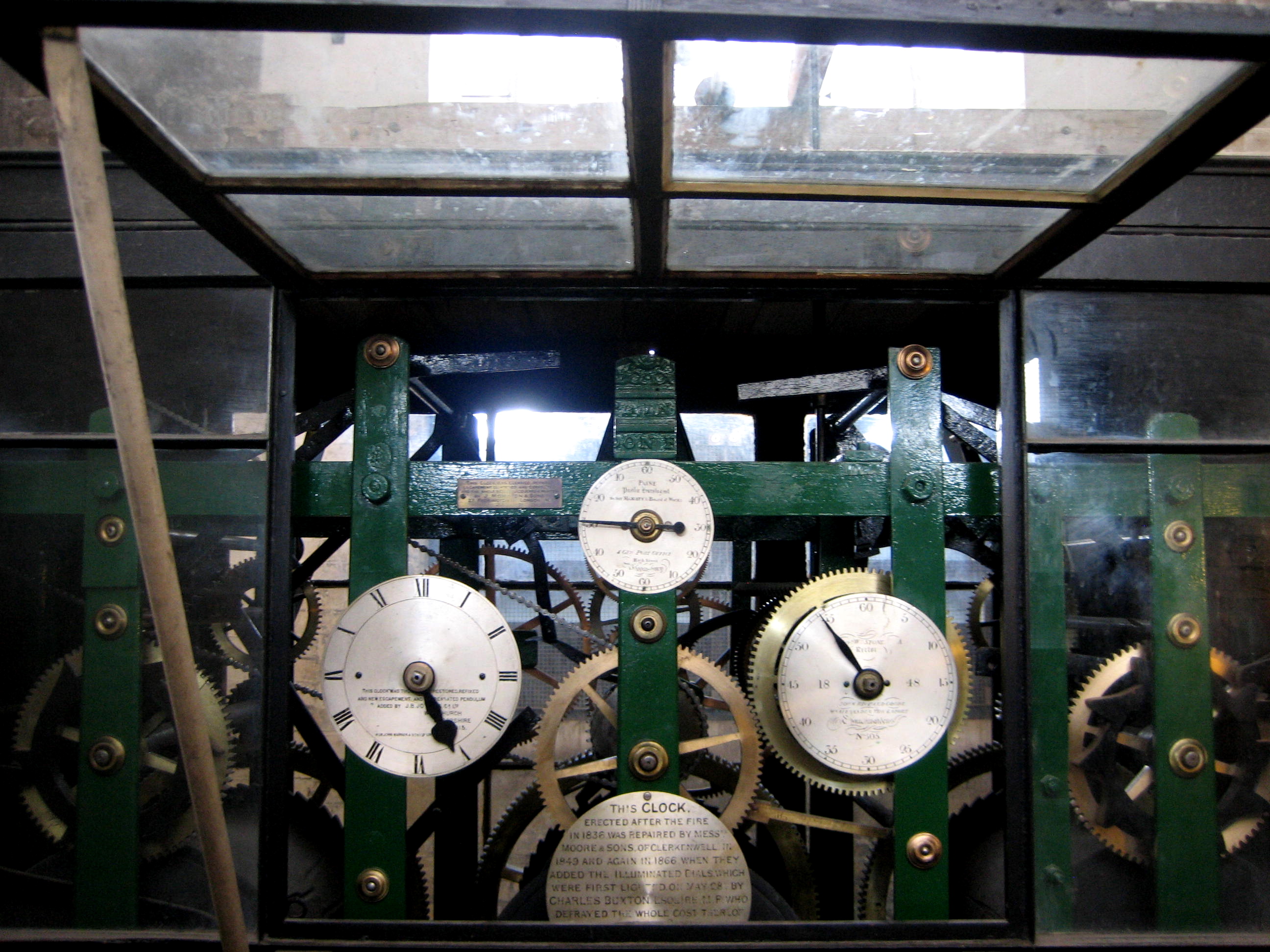
No-one has much cause to come up here and, when we reached the door at the top of the stairs, the verger was unsure of his keys. As I recovered my breath from the climb, while he tried each key in turn upon the ring until he was successful, I listened to the dignified tick coming from the other side of the door. When he opened the door, I discovered it was the sound of the lonely clock that has measured out time in Spitalfields since 1836 from the square room with an octagonal roof beneath the pinnacle of the spire. Lit only by diffuse daylight from the four clock faces, the renovations that have brightened up the rest of the church do not register here.
Once we were inside, the verger opened the glazed case containing the gleaming brass wheels of the mechanism, turning with inscrutable purpose within their green-painted steel cage, driving another mechanism in a box up above that rotates the axles, turning the hands upon each of the clock faces. Not a place for human occupation, it was a room dedicated to time and, as intervention is required only rarely here, we left the clock to run its course in splendid indifference.
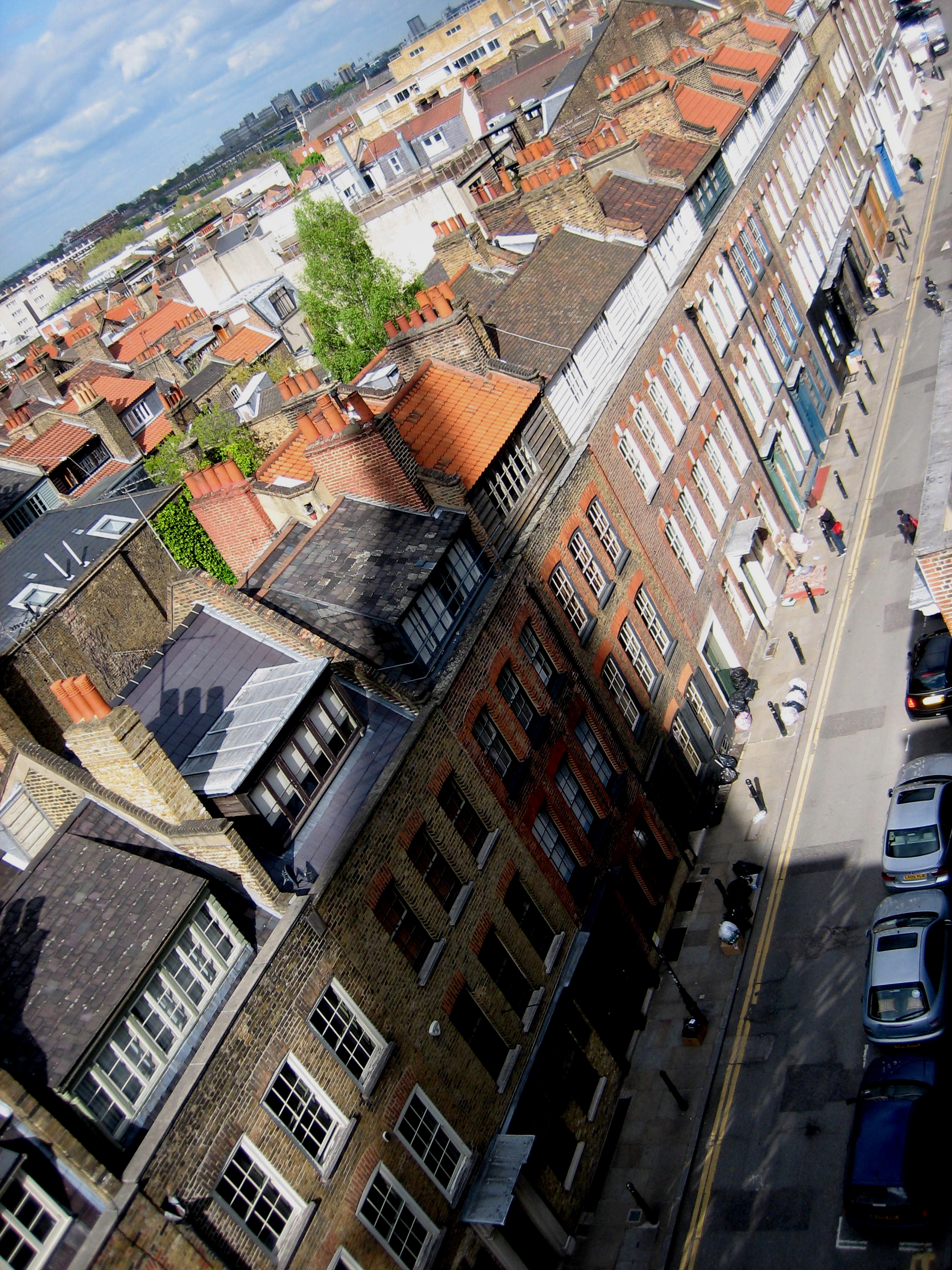
By contrast, a walk along the ridge of the roof of Christ Church, Spitalfields, presented a chaotic and exhilarating symphony of sensations, buffered by gusts of wind beneath a fast-moving sky that delivered effects of light changing every moment. It was like walking in the sky. On the one hand, Fashion St and on the other Fournier St, where the roofs of the eighteenth century houses topped off with weavers’ lofts create an extravagant roofscape of old tiles and chimney pots at odd angles. Liberated by the experience, I waved across the chasm of the street to residents of Fournier St in their rooftop gardens opposite, just like waving to people from a train.
Returning to the body of the church, we explored a suite of hidden vestry rooms behind the altar, magnificently proportioned apartments to encourage lofty thoughts, with views into the well-kept rectory garden. From here, we descended into the crypt constructed of brick vaults to enter the cavernous spaces that until recent years were stacked with human remains. Today these are innocent, newly-renovated spaces without any tangible presence to recall the thousands who were laid to rest here until it was packed to capacity and closed for burial in 1812 by Rev William Stond MA, as confirmed by a finely lettered stone plaque.
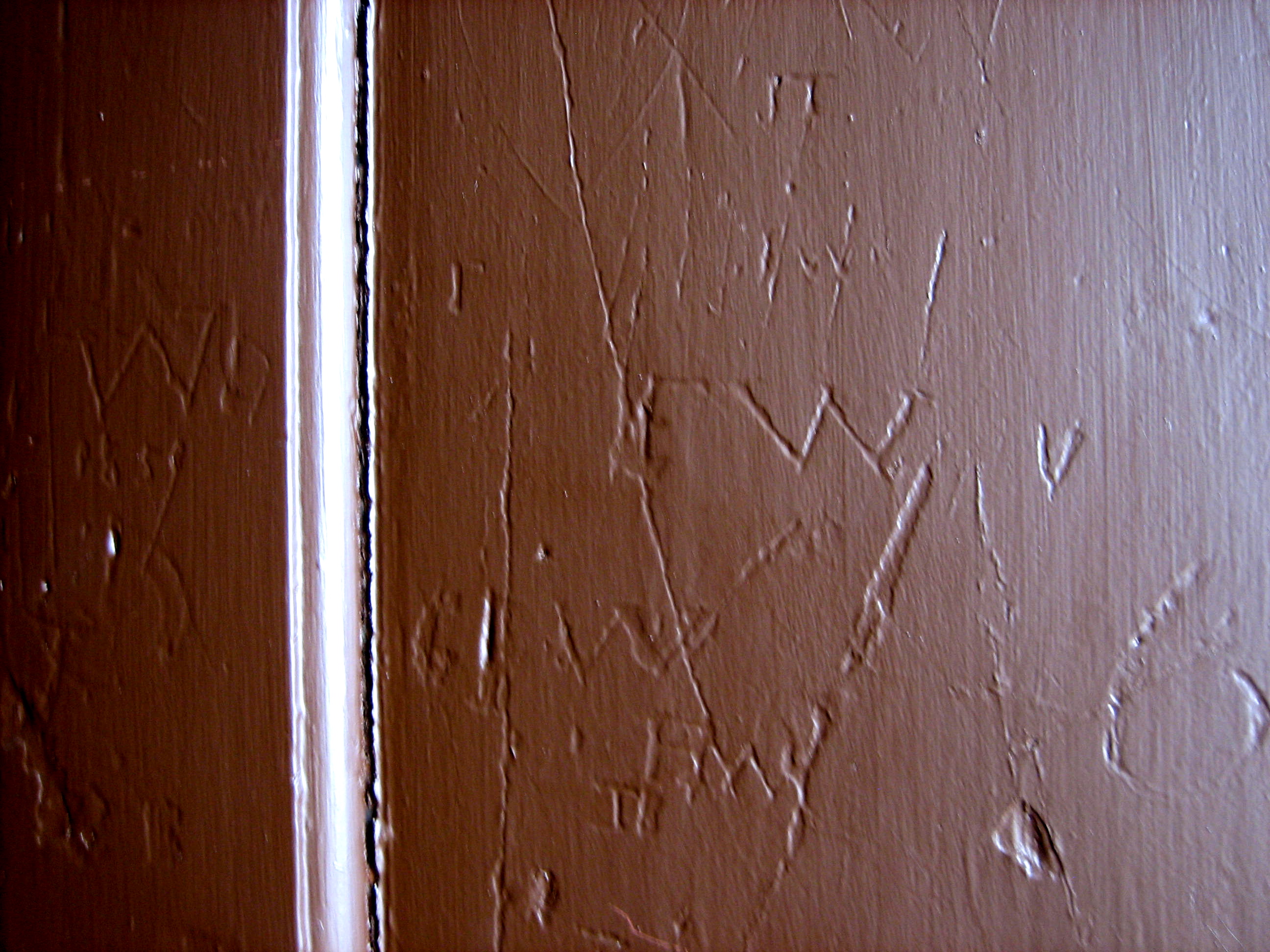
Passing through the building, up staircases, through passages and in each of the different spaces from top to bottom, there were so many of these plaques of different designs in wood and stone, recording those were buried here, those who were priests, vergers, benefactors, builders and those who rang the bells. In parallel with these demonstrative memorials, I noticed marks in hidden corners, modest handwritten initials, dates and scrawls, many too worn or indistinct to decipher. Everywhere I walked, so many people had been there before me, and the crypt and vaults were where they ended up.
My visit started at the top and I descended through the structure until I came, at the end of the afternoon, to the small private vaults constructed in two storeys beneath the porch, where my journey ended, as it did in a larger sense for the original occupants. These delicate brick vaults, barely three feet high and arranged in a crisscross design, were the private vaults of those who sought consolation in keeping the family together even after death. All cleaned out now, with modern cables and pipes running through, I crawled into the maze of tunnels and ran my hand upon the vault just above my head. This was the grave where no daylight or sunshine entered, and it was not a place to linger on a bright afternoon in August.
Christ Church gave me a journey through many emotions, and it fascinates me that this architecture can produce so many diverse spaces within one building and that these spaces can each reflect such varied aspects of the human experience, all within a classical structure that delights the senses through the harmonious unity of its form.
The mechanism of this clock runs so efficiently that it only has to be wound a couple of times each year
Looking up inside the spire
A model of the rectory in Fournier St
On the reverse of the door of the organ cupboard
In the vestry
For nearly three centuries, the shadow of the spire has travelled the length of Fournier St each afternoon
You may also like to read about
Glenys Bristow In Spitalfields
Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
Glenys with her dad Stanley Arnabaldi in their cafe at 100 Commercial St
When I met Glenys Bristow (1922-2017), she did not live in Spitalfields anymore but in a well-kept flat in a quiet corner of Bethnal Green. Glenys might never even have come to Spitalfields if the Germans had not dropped a bomb on her father’s cafe in Mansell St, down below Aldgate. In fact, Glenys would have preferred to stay in Westcliff-on-Sea and never come to London at all, if she had been given the choice. Yet circumstances prevailed to bring Glenys to Spitalfields. And, as you can see from this picture taken in 1943 – in the cafe she ran with her father opposite the market – Glenys embraced her life in Spitalfields wholeheartedly.
“I came to London from Westcliff-on-Sea when I was fifteen. I didn’t like London at all. At first we were in Limehouse, I walked over to Salmon Lane and there was Oswald Mosley making a speech to his blackshirts. The police told us to go home. I was sixteen and I missed Westcliff so, me and my friend, we took a job in a cafe there for the Summer. We were naive. We weren’t streetwise. We didn’t have confidence like kids do today.
The family moved to Mansell St where had a cafe – our first cafe – and we lived above it. My father’s name was Arnabaldi, I used to hate it when I was at school. My father always wanted to have a cafe of his own. His father had come over from Italy and ran a shop in Friern Barnet but died when my father was only eleven, and my father told me his mother died young of a broken heart.
In September 1940, we were bombed out of Mansell St. Luckily no-one was inside at the time because it was the weekend. It was a big shock. My mother, sister Rita and brother Raymond had gone to Wales to visit my grandparents in the Rhonda Valley. I’d left that afternoon with my husband Jack, who was my boyfriend then. We had something to eat at his sister’s then we went by bus to my future in laws at Old St, where we slept in an Anderson shelter. On Monday morning, we were walking back to Mansell St and these people asked, “Where are you going?” I said, “Home, I’m going to change before going to work.” “You’ll be lucky,” they said. When we got there we found the site roped off. It was all gone. Just a pile of rubble.”
Glenys got married at eighteen years old at Arbour Sq Registry Office when Jack was enlisted.”We didn’t know if we were going to be here from one day to the next,”she told me, describing her experience of living through the blitz, suffering the destruction of her home in the bombing and then finding herself alone with a baby while her husband was at war.
“In late 1942, my father got the cafe at 100 Commercial St, Spitalfields, and I was living in a little house in Vallance Rd and had my first baby John and he was just eleven months old. My father bought the cafe and he arranged for me to stay in the top floor flat next door at 102, Commercial St. We just had two rooms above some offices with a cooker on the landing and a toilet. When the air raid sirens went, I didn’t want to get out of bed so my dad fixed up a bell on a string from next door. I used to wrap my baby in an eiderdown and wait until the shrapnel had stopped flying before I went out of the door into the street to the cafe next door.
I did a bit of everything, cooking, serving behind the counter. People came in from the Godfrey & Phillips cigarette factory, the market and all the workshops. The fruit & vegetable market kept going all through the war but, because of the blackout, it started later in the night. We were lucky being close to the market, we were never short of anything.
At the end of the war, Jack came back and worked for my parents until, after a few years, the lease on the cafe ran out and we had to give it up. In 1956, we rented a little cafe in Hanbury St that belonged to the Truman Brewery, but we were only there three years before we had to move again because they had expansion plans. We bought the cafe opposite where Bud Flanagan had been born and called it Jack’s Cafe. And we were there from 1960 until 1971.
Because of the market, we had to have dinner ready to serve at nine in the morning, and again from twelve ’til two. Nothing was frozen, everything was cooked daily and Jack used to buy everything fresh from the market. They said we had the best and the cleanest cafe in the Spitalfields Market, and a lot of our customers became friends. My daughter met her husband there, he was a porter – his whole family were porters – and my son went to work as a porter, he was called an empty boy until he got his badge.
I just took it for granted. We used to open at half past four in the morning and I used to try and get cleaned up by half past six at night. It was very hard. Eventually, we sold it because I had back trouble and my husband bought a couple of lorries. In 1976, we moved from Commercial St to Chicksand St. I had four children altogether, only three that lived.
When it all changed, we went back – my daughter and I – to visit our old cafe. It had the same formica on the wall my husband had put up and I kept trying to look in the kitchen. I loved it when we worked for my mum and dad, and when we had our own place. I loved it and I miss it. They said I was the best pastry cook in Spitalfields.”
Glenys Bristow was a woman of astonishing resilience, possessing quick wits and a bright intelligence. Random events delivered her to Spitalfields in wartime, where she found herself at the centre of a lively working community. Losing everything when the bomb fell on her father’s cafe, and living day-to-day in peril of her life, she summoned extraordinary strength of character, bringing up her family and working long hours too. Glenys had no idea that she would live into another century, and enjoy the advantage of living peacefully in Bethnal Green and be able to look back on it all with affection.
Glenys Bristow (1922-2017)
Glenys’ home in Mansell St after the bomb dropped in 1940.
At the cafe in Mansell St.
Glenys and her daughter Linda, 1950
Glenys and Linda visit the site of the former cafe in Mansell St, 1951.
Glenys with her children, John, Linda and Alan.
Glenys and her husband Jack with their first car.
Stan, Jack, Glenys and her mother Anne on a day trip to Broxbourne.
Glenys’ identity card with Commercial Rd mistakenly substituted for Commercial St.
Glenys with her granddaughter Sue Bristow.
You may also like to read about