The Return Of Benjamin Pollock

Benjamin Pollock’s Toy Shop at 73 Hoxton Market was destroyed by bombing in 1944 but this autumn its magical interior is reimagined at Dennis Severs’ House from 4th October until 10th November. Designed in collaboration with Pollock’s Toy Museum, the garden room of 18 Folgate Street will be transformed by a joyous cast of 19th-century toy-theatre characters and backgrounds alongside a Victorian printing press, finely-engraved copper plates, Mr Redington’s original box of pigments, Pollock’s own storage boxes and antique toy theatres hung from the walls and ceiling.
In November, you can attend toy theatre performances at Museum of the Home in Hoxton, The Bottle Imp on Saturday 1st and Dick Whittington and Cinderella on Sunday 24th. By employing copies of the extremely rare 1830s ‘twopence coloured’ sheets, and the authentic reduced script, the effect of the original stage plays will be recreated.
In December, Townhouse Spitalfields will be hosting a Pollock’s Toy Museum pop-up shop.
Today The Gentle Author outlines the history of toy theatres in the East End.

Benjamin Pollock outside his shop in Hoxton Market
THE TOY THEATRES OF HOXTON & SHOREDITCH
These days, Old St is renowned for its digital industries but – for over a hundred years – this area was celebrated as the centre of toy theatre manufacture in London. Formerly, these narrow streets within walking distance of the City of London were home to highly skilled artisans who could turn their talents to the engraving, printing, jewellery, clock, gun and instrument-making trades which operated here – and it was in this environment that the culture of toy theatres flourished.
Between 1830 and 1945, at a handful of addresses within a half mile of the junction of Old St and City Rd, the modest art of publishing engraved plates of characters and scenery for Juvenile Dramas enjoyed its heyday. The names of the protagonists were William Webb and Benjamin Pollock. The overture was the opening of Archibald Park’s shop at 6 Old St Rd in 1830, and the drama was brought to the public eye by Robert Louis Stevenson in his essay A Penny Plain and Twopence Coloured in 1884, before meeting an ignominious end with the bombing of Benjamin Pollock’s shop in Hoxton St in 1945.
Responsibility for the origin of this vein of publishing belongs both to John Kilby Green of Lambeth and William West of Wych St in the Strand, with the earliest surviving sheets dated at 1811. Green was just an apprentice when he had the notion to produce sheets of theatrical characters but it was West who took the idea further, publishing plates of popular contemporary dramas. From the beginning, the engraved plates became currency in their own right and many of Green’s vast output were later acquired by Redington of Hoxton and eventually published there as Pollock’s. West is chiefly remembered for commissioning artists of acknowledged eminence to design plates, including the Cruickshank brothers, Henry Flaxman, Robert Dighton and – most notably – William Blake.
Green had briefly collaborated to open Green & Slee’s Theatrical Print Warehouse at 5 Artillery Lane, Spitalfields, in 1805 to produce ‘The Tiger’s Horde’ but the first major publishers of toy theatres in the East End were Archibald Park and his family, rising to prosperity with premises in Old St and then 47 Leonard St between 1830 until 1870.
Park’s apprentice from 1835-42, William Webb, set up on his own with shops in Cloth Fair and Bermondsey before eventually opening a quarter a mile from his master at 49 (renumbered as 146) Old St in 1857. Webb traded here until his death in 1898 when his son moved to 124 Old St where he was in business until 1931. Contrary to popular belief, it was William Webb who inspired Robert Louis Stevenson’s famous essay upon the subject of toy theatres. Yet a disagreement between the two men led to Stevenson approaching Webb’s rival Benjamin Pollock in Hoxton St, who became the subject of the story instead and whose name became the byword for toy theatres.
In 1876, at twenty-one years old, Benjamin Pollock had the good fortune to acquire by marriage the shop opened by his late father-in-law, John Redington in Hoxton in 1851. Redington had all the theatrical plates engraved JK Green and, in time, Benjamin Pollock altered these plates, erasing the name of ‘Redington’ and replacing it with his own just as Redington had once erased the name ‘Green’ before him. Although it was an unpromising business at the end of the nineteenth century, Pollock harnessed himself to the work, demonstrating flair and aptitude by producing high quality reproductions from the old plates, removing ‘modern’ lettering applied by Redington and commissioning new designs from the naive artist James Tofts.
In 1931, the writer AE Wilson had the forethought to visit Webb’s shop in Old St and Pollock’s in Hoxton St, talking to William Webb’s son Harry and to Benjamin Pollock, the last representatives of the two surviving dynasties in the arcane world of Juvenile Dramas. “In his heyday, his business was very flourishing,” admitted Harry Webb speaking of his father,” Why, I remember we employed four families to do the colouring. There must have been at least fifteen people engaged in the work. I could tell their work apart, no two of them coloured alike. Some of the work was beautifully done.”
Harry recalled visits by Robert Louis Stevenson and Charles Dickens to his father’s premises. “Up to the time of the quarrel, Stevenson was a frequent visitor to the shop, he was very fond of my father’s plays. Indeed it was my father who supplied the shop in Edinburgh from which he bought his prints as a boy,” he told Wilson.
Benjamin Pollock was seventy-five years old when Wilson met him and ‘spoke in strains not unmingled with melancholy.’ “Toy theatres are too slow for the modern boy and girl,” he confessed to Wilson, “even my own grandchildren aren’t interested. One Christmas, I didn’t sell a single stage.” Yet Pollock spoke passionately recalling visits by Ellen Terry and Charlie Chaplin to purchase theatres. “I still get a few elderly customers,” Pollock revealed, “Only the other day, a City gentleman drove up here in a car and bought a selection of plays. He said he had collected them as a boy. Practically all the stock has been here fifty years or so. There’s enough to last out my time, I reckon.”
Shortly after AE Wilson’s visit to Old St & Hoxton, Webb’s shop was demolished while Benjamin Pollock struggled to earn even the rent for his tiny premises until his death in 1937. Harry Webb lived on in Caslon St – named after the famous letter founder who set up there two centuries earlier – opposite the site of his father’s Old St shop until his death in 1962.
Robert Louis Stevenson visited 73 Hoxton St in 1884. “If you love art, folly or the bright eyes of children speed to Pollock’s” he wrote fondly afterwards. Stevenson was an only child who played with toy theatres to amuse himself in the frequent absences from school due to sickness when he was growing up in Edinburgh. I too was an only child enchanted by the magic of toy theatres, especially at Christmas, but I cannot quite put my finger on what still draws me to the romance of them.
Even Stevenson admitted “The purchase and the first half hour at home, that was the summit.” As a child, I think the making of them was the greater part of the pleasure, cutting out the figures and glueing it all together. “I cannot deny the joy that attended the illumination, nor can I quite forget that child, who forgoing pleasure, stoops to tuppence coloured,” Stevenson concluded wryly. I cannot imagine what he would have made of Old St’s ‘Silicon Roundabout’ today.

Drawings for toy theatre characters by William Blake for William West

The sheet as published by William West, November 4th 1816 – note Blake’s initials, bottom right
 Another sheet engraved after drawings by William Blake, 1814
Another sheet engraved after drawings by William Blake, 1814

124 Old St, 1931




73 Hoxton St (formerly 208 Hoxton Old Town) 1931

Benjamin Pollock at his shop on Hoxton St in 1931



An Invitation From The Gentle Author
THIS IS NOW FULL BUT THERE WILL BE FURTHER EVENTS FOR THIS BOOK THROUGH THE AUTUMN & THE EXHIBITION RUNS UNTIL 30th MARCH


Down A Well In Spitalfields

Thirty years ago, eighteen wooden plates and bowls were recovered from a silted-up well in Spitalfields. One of the largest discoveries of medieval wooden vessels ever made in this country, they are believed to be dishes belonging to the inmates of the long-gone Hospital of St Mary Spital, which gave its name to this place. After seven hundred years lying in mud at the bottom of the well, the thirteenth century plates were transferred to the London Museum store in Hoxton where I went to visit them as a guest of Roy Stephenson, Head of Archaeological Collections.
Almost no trace remains above ground of the ancient Hospital of St Mary yet, in Spital Sq, the roads still follow the ground plan laid laid out by Walter Brune in 1197, with the current entrance from Bishopsgate coinciding to the gate of the Priory and Folgate St following the line of the northern perimeter wall. Stand in the middle of Spital Sq today, and you are surrounded by glass and steel corporate architecture, but seven hundred years ago this space was enclosed by the church of St Mary and then you would be standing in the centre of the aisle where the transepts crossed beneath the soaring vault with the lantern of the tower looming overhead. Stand in the middle of Spital Sq today, and the Hospital of St Mary is lost in time.
In his storehouse, Roy Stephenson had eleven miles of rolling shelves that contain all the finds excavated from old London in recent decades. He opened one box containing bricks in a plastic bag that originated from Pudding Lane and were caked with charcoal dust from the Fire of London. I leant in close and a faint cloud of soot rose in the air, with an unmistakable burnt smell persisting after four centuries. “I can open these at random,” said Roy, gesturing towards the infinitely receding shelves lined with boxes in every direction, “and every one will have a story inside.”
Removing the wooden plates and bowls from their boxes, Roy laid them upon the table for me to see. Finely turned and delicate, they still displayed ridges from the lathe, seven centuries after manufacture. Even distorted by water and pressure over time, it was apparent that, even if they were for the lowly inhabitants of the hospital, these were not crudely produced items. At hospitals, new arrivals were commonly issued with a plate or bowl, and drinking cup and a spoon. Ceramics and metalware survive but rarely wood, so Roy is especially proud of these humble platters. “They are a reminder that pottery is a small part of the kitchen assemblage and people ate off wood and also off bread which leaves no trace.” he explained. Turning over a plate, Roy showed me a cross upon the base made of two branded lines burnt into the wood. “Somebody wanted to eat off the same plate each day and made it their own,” he informed me, as each of the bowls and plates were revealed to have different symbols and simple marks upon them to distinguish their owners – crosses, squares and stars.
Contemporary with the plates, there were a number of ceramic jugs and flagons which Roy produced from boxes in another corner of his store. While the utilitarian quality of the dishes did not speak of any precise period, the rich glazes and flamboyant embossed designs, with studs and rosettes applied, possessed a distinctive aesthetic that placed them in another age. Some had protuberances created with the imprints of fingers around the base that permitted the jar to sit upon a hot surface and heat the liquid inside without cracking from direct contact with the source of heat, and these pots were still blackened from the fire.
The intimacy of objects that have seen so much use conjures the presence of the people who ate and drank with them. Many will have ended up in the graveyard attached to the hospital and then were exhumed in the nineties. It was the largest cemetery ever excavated and their remains are now stored in the tall brick rotunda where London Wall meets Goswell Rd outside the Museum of London. This curious architectural feature that serves as a roundabout is in fact a mausoleum for long dead Londoners and, of the seventeen thousand souls whose bones are there, twelve thousand came from Spitalfields.
The Priory of St Mary Spital stood for over four hundred years until it was dissolved by Henry VIII who turned its precincts into an artillery ground in 1539. Very little detail is recorded of the history though we do know that many thousands died in the great famine of 1258, which makes the survival of these dishes at the bottom of a well especially plangent.
Returning to Spitalfields, I walked again through Spital Sq. Yet, in spite of the prevailing synthetic quality of the architecture, the place had changed for me after I had seen and touched the bowls that once belonged to those who called this place home seven centuries ago – and thus the Hospital of St Mary Spital was no longer lost in time.
Sixteenth century drawing of St Mary Spital as Shakespeare may have known it, with gabled wooden houses lining Bishopsgate.
“Nere and within the citie of London be iij hospitalls or spytells, commonly called Seynt Maryes Spytell, Seynt Bartholomewes Spytell and Seynt Thomas Spytell, and the new abby of Tower Hyll, founded of good devocion by auncient ffaders, and endowed with great possessions and rents onley for the releffe, comfort, and helyng of the poore and impotent people not beyng able to help themselffes, and not to the mayntennance of chanins, preestes, and monks to lyve in pleasure, nothyng regardyng the miserable people liying in every strete, offendyng every clene person passyng by the way with theyre fylthy and nasty savours.” Sir Richard Gresham in a letter to Thomas Cromwell, August 1538
Finely turned ash bowl.
Fragment of a wooden plate
Turned wooden plate marked with a square on the base to indicate its owner.
Copper glazed white ware jug from St Mary Spital
Redware glazed flagon, used to heat liquid and still blackened from the fire seven hundred years later.
White ware flagon, decorated in the northern French style.
A pair of thirteenth century boots found at the bottom of the cesspit in Spital Sq.
The gatehouse of St Mary Spital coincides with the entrance to Spital Sq today and Folgate St follows the boundary of the northern perimeter .
Bruyne:
- My vowes fly up to heaven, that I would make
- Some pious work in the brass book of Fame
- That might till Doomesday lengthen out my name.
- Near Norton Folgate therefore have I bought
- Ground to erect His house, which I will call
- And dedicate St Marie’s Hospitall,
- And when ’tis finished, o’ r the gates shall stand
- In capitall letters, these words fairly graven
- For I have given the worke and house to heaven,
- And cal’d it, Domus Dei, God’s House,
- For in my zealous faith I now full well,
- Where goode deeds are, there heaven itself doth dwell.
(Walter Brune founding St Mary Spital from ‘A New Wonder, A Woman Never Vexed’ by William Rowley, 1623)
You may also like to read about
Harry T Harmer, Artist


St Botolph’s Without Aldgate, 1963
The facts of the life of Harry T. Harmer (1927-2013) are scarce yet his distinctive paintings speak eloquently of his personal vision. Born in Kennington, Harry was afflicted with epilepsy and married his wife Ruby when they were both in their adolescence. Ruby offered Harry emotional support in the face of a father who did not recognise his disorder and the couple enjoyed a marriage that lasted through eight decades.
Disqualified from military service, Harry worked in the parks department and, possessing a strong sense of justice, he fought for the rights of fellow workers through many years as a union representative. In the mid-fifties, Harry discovered an ability to draw and paint, travelling around Kennington and north of the river to the East End, making sketches of places that embodied the living city he knew intimately.
Harry had his first exhibition in 1963 and continued to paint and show his works for the rest of his life. Although sometimes described as a naive artist, it is obvious that the sensibility behind Harry’s painting is far from unsophisticated. His compelling pictures are concerned with more than straightforward representation of places, offering instead emotional landscapes of the lives of working people rendered in his own individual style.
Ruby kept Harry’s treasured copy of the drawings of L. S. Lowry in two volumes as a token of his major artistic influence. Yet Harry forged a visual language of his own, placing his curious bird-like figures strategically within a delicately painted streetscape that appears on the point of dissolving.
For most of their married life, Harry and Ruby Harmer occupied a council flat in a dignified Victorian terrace in Kennington, where Ruby lived on tending to an appealingly unkempt garden and a posse of neighbourhood cats. In the back room overlooking the garden where Harry did his paintings, his small formica topped work table stood by the window where a box of his ashes sat beside a bunch of fresh flowers that Ruby changed each week. The popularity of Harry’s works meant that Ruby was the devoted custodian of just a few of her husband’s paintings, and a suitcase of his pencil sketches, press cuttings and exhibition catalogues.

Wellclose Sq, 1962

St Katharine’s Way, 1962

Cable St, 1962

Harry T. Harmer, 2009
Paintings copyright © Ruby Harmer
Published courtesy of Tower Hamlets Local History Library & Archives
Take a look at some of the other artists featured in East End Vernacular
John Thomas Smith’s Rural Cottages


Near Battlebridge, Middlesex
As September draws to a close and autumn closes in, I get the urge to go to ground, hiding myself away in some remote cabin and not straying from the fireside until spring shows again. With this in mind, John Thomas Smith’s twenty etchings of extravagantly rustic cottages published as Remarks On Rural Scenery Of Various Features & Specific Beauties In Cottage Scenery in 1797 suit my hibernatory fantasy ideally.
Born in the back of a Hackney carriage in 1766, Smith grew into an artist consumed by London, as his inspiration, his subject matter and his life. At first, he drew the old streets and buildings that were due for demolition at the turn of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries in Ancient Topography of London and Antiquities of London, savouring every detail of their shambolic architecture with loving attention. Later, he turned his attention to London streetlife, the hawkers and the outcast poor, portrayed in Vagabondiana and Remarkable Beggars, creating lively and sympathetic portraits of those who scraped a living out of nothing but resourcefulness. By contrast, these rural cottages were a rare excursion into the bucolic world for Smith, although you only have to look at the locations to see that he did not travel too far from the capital to find them.
“Of all the pictoresque subjects, the English cottage seems to have obtained the least share of particular notice,” wrote Smith in his introduction to these plates, which included John Constable and William Blake among the subscribers, “Palaces, castles, churches, monastic ruins and ecclesiastical structures have been elaborately and very interestingly described with all their characteristic distinctions while the objects comprehended by the term ‘cottage scenery’ have by no means been honoured with equal attention.”
While emphasising that beauty was equally to be found in humble as well as in stately homes, Smith also understood the irony that a well-kept dwelling offered less picturesque subject matter than a derelict hovel. “I am, however, by no means cottage-mad,” he admitted, acknowledging the poverty of the living conditions, “But the unrepaired accidents of wind and rain offer far greater allurements to the painter’s eye, than more neat, regular or formal arrangements could possibly have done.”
Some of these pastoral dwellings were in places now absorbed into Central London and others in outlying villages that lie beneath suburbs today. Yet the paradox is that these etchings are the origin of the romantic image of the English country cottage which has occupied such a cherished position in the collective imagination ever since, and thus many of the suburban homes that have now obliterated these rural locations were designed to evoke this potent rural fantasy.

On Scotland Green, Ponder’s End

Near Deptford, Kent

At Clandon, Surrey – formerly the residence of Mr John Woolderidge, the Clandon Poet

In Bury St, Edmonton

Near Jack Straw’s Castle, Hampstead Heath

In Green St, Enfield Highway

Near Palmer’s Green, Edmonton
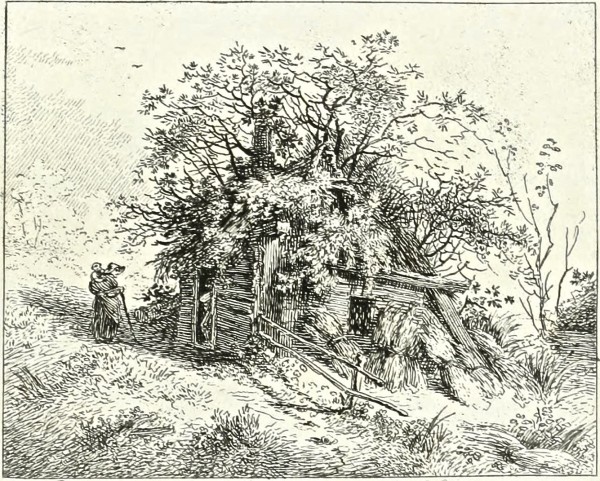
Near Ranelagh, Chelsea

In Green St, Enfield Highway

At Ponder’s End, Near Enfield

On Merrow Common, Surrey

At Cobham, Surrey – in the hop gardens

Near Bull’s Cross, Enfield

In Bury St, Edmonton

On Millbank, Westminster

Near Edmonton Church

Near Chelsea Bridge

In Green St, Enfield Highway

Lady Plomer’s Place on the summit of Hawke’s Bill Wood, Epping Forest

You may also like to take a look at these other works by John Thomas Smith
John Thomas Smith’s Ancient Topography of London
John Thomas Smith’s Antiquities of London
John Thomas Smith’s Vagabondiana
John Thomas Smith’s Vagabondiana II
Colin O’Brien At Chats Palace
There is currently a posthumous exhibition of work by former Contributing Photographer Colin O’Brien at Chats Palace, 42-44 Brooksby’s Walk, E9 6DF. Colin had an affinity with young people and this show focusses on his photography of children in the post-war years. Curator Peter Young introduces the exhibition.
‘I first came across Colin and his photography in December 2006 when he exhibited at the Oxo Tower Gallery. The walls were packed with strong black and white images of working class life in London and beyond, portrayed in a straightforward and dignified humanist style.
Colin was on hand to chat and showed me a portfolio of prints which was where I first saw ‘Lady in a summer dress Chatsworth Rd 1980s.’ Benjamin the chemist plus the landmark clock, and Percy Ingle the baker, were all present and correct in the background. I had walked down that street for twenty years. This was by far the best picture I had seen which summed up the atmosphere of unexpected and quiet beauty that pervaded the urban backwater of Homerton and Clapton at that time.
In 2015, Colin became a patron of Chats Palace and the following year a small exhibition of his work was installed in the recently refurbished Blue Room where it hangs to this day. As with all his work, it shows the people of London in all their multifarious ethnic and cultural, working and non-working forms. Inquisitive, outward looking and confident.’ – Peter Young







Colin’s photograph of his pals, taken in 1948 at the age of eight in Hatton Garden.

Photographs copyright © Estate of Colin O’Brien
Take a look at more pictures by Colin O’Brien
Travellers’ Children in London Fields
Marie Lenclos’ Still Light
Artist Marie Lenclos introduces her new exhibition of paintings Still Light which opens at Townhouse this Saturday 28th September and runs until Sunday 13th October

Blue Door, Fournier St
‘When I first came to London in the nineties as an Erasmus student, Spitafields immediately became a favourite place to explore. For a young Parisian, there was magic in its dense urban fabric. Brick Lane was where you went to find a cheap bike or pick up old crockery. There were surprises at every corner, human stories or colourful stalls, and the tall town houses loomed over you with the weight of their past. I liked the fact I was a foreigner amongst many others.
This was before the creation of the Overground which opened a whole new transport route for me between my home in Denmark Hill and an area of London I still love to get lost in. I walk down Fournier St and the whole place feels like a museum to me, every street corner evokes a scene from another era. The industrial past is ever present and the richness of old brickwork is illuminated by the fleeting sunlight.
These oil paintings are a record of what I notice when I walk these streets. There is noise everywhere, the perpetual movement of passers by, hurried workers carrying coffees, cars starting and stalling, suddenly honking. But to me, there is only calm. When I focus on the scene in front of me, with its play of light and its colourful texture, it is like a mental pause.
My paintings are urban landscapes caught in a moment of calm amongst the chaos. Light is the most important actor, its role is to reveal the permanence and unexpected beauty.’ – Marie Lenclos

Red shutters, Fournier St

Lamp Post, Fournier St

Window, Spitalfields

View from a house on Princelet St

Brick patchwork, Off Columbia Rd

Across Old St, Shoreditch

Telephone Exchange, Shoreditch

Blue Gate, Kingsland Rd

Near Hoxton Station

Hoxton Arches

Posters, Shoreditch

Paintings copyright © Marie Lenclos
You my also like to take a look at
























































