A Visit To Great Tom At St Paul’s

Book now for my tours through August, September & October

Like bats, bells lead secluded lives hibernating in dark towers high above cathedrals and churches. Thus it was that I set out to climb to the top of the south west tower of St Paul’s Cathedral last week to visit Great Tom, cast by Richard Phelps at the Whitechapel Bell Foundry in 1716.
At 11,474lbs, Great Tom is significantly smaller than Great Paul, its neighbour in the tower at 37,483lbs, yet Great Paul has been silent for many years making Great Tom the largest working bell at St Paul’s and, if Big Ben (30,339lbs) falls silent during renovations this year, then Great Tom will become London’s largest working bell.
To reach Great Tom, I had first to climb the stone staircase beneath the dome of St Paul’s and then walk along inside the roof of the nave. Here, vast brick hemispheres protrude as the reverse of the shallow domes below, creating a strange effect – like a floor of a multi-storey car park for flying saucers. At the west end, a narrow door leads onto the parapet above the front of the cathedral and you descend from the roof of the nave to arrive at the entrance to the south west tower, where a conveniently placed shed serves as a store for spare clock hands.
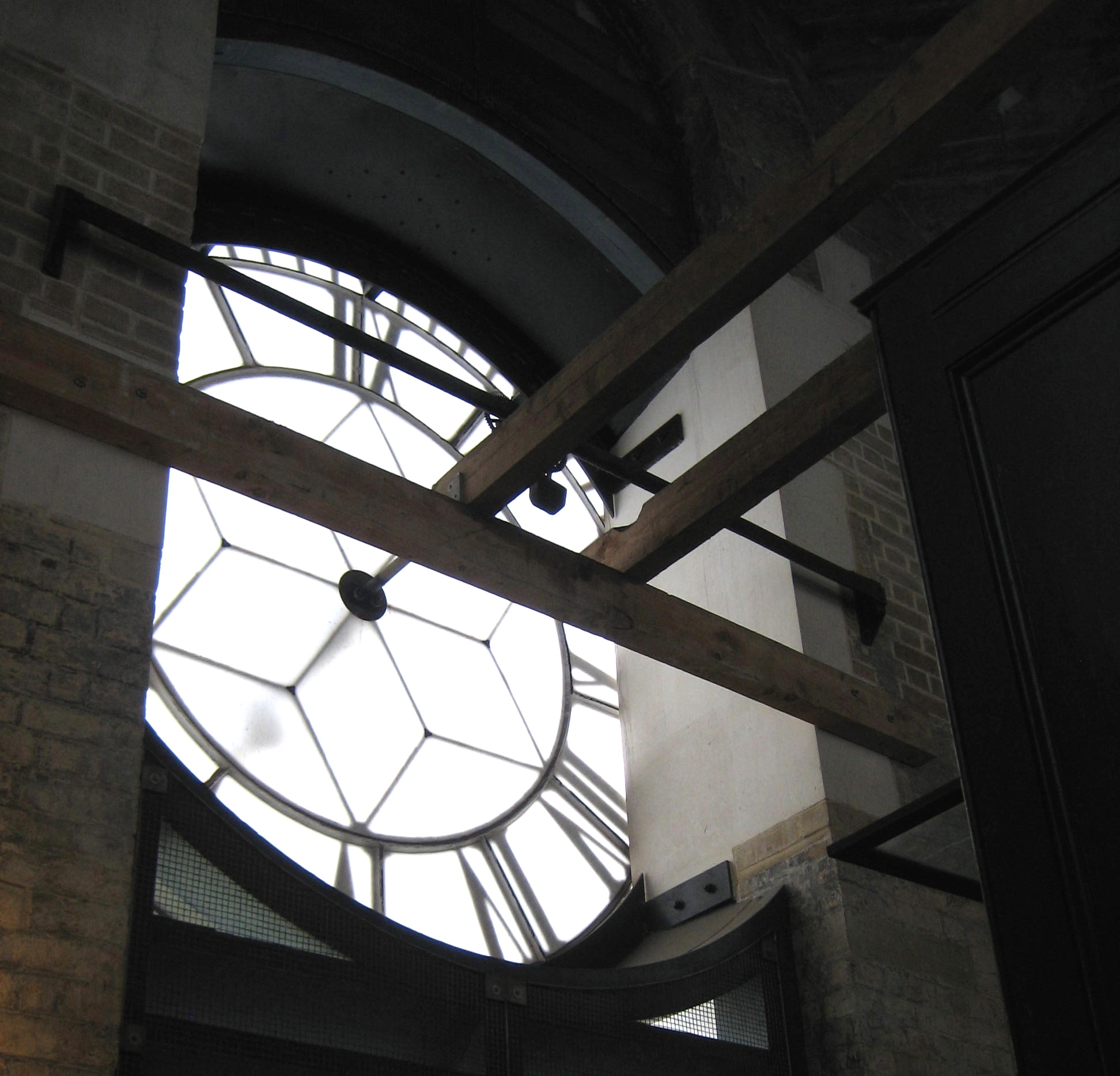
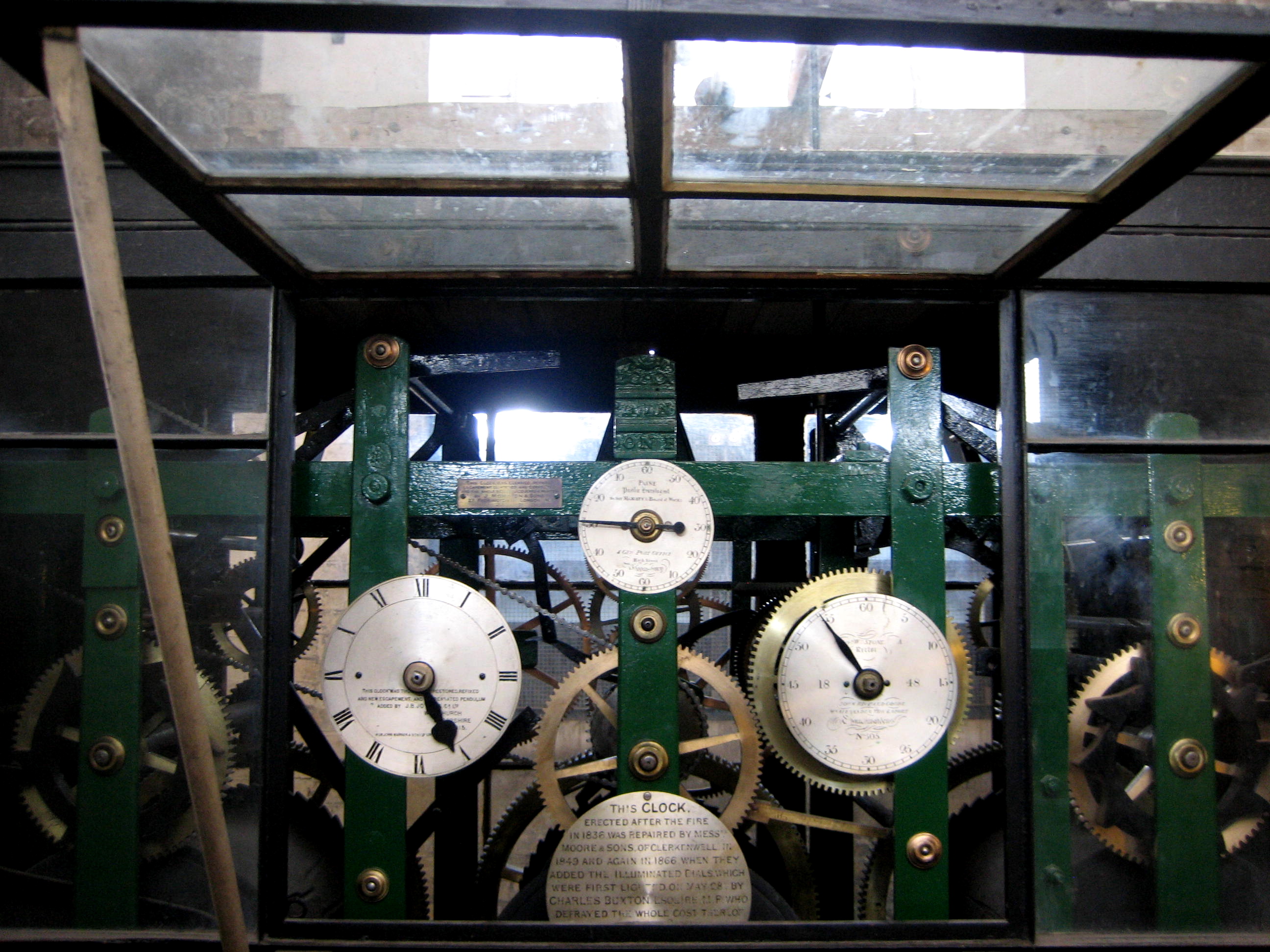
Inside the stone tower is a hefty wooden structure that supports the clock and the bells above. Here I climbed a metal staircase to take a peek at Great Paul, a sleek grey beast deep in slumber since the mechanism broke years ago. From here, another stone staircase ascends to the open rotunda where expansive views across the city induce stomach-churning awe. I stepped onto a metal bridge within the tower, spying Great Paul below, and raised my eyes to discern the dark outline of Great Tom above me. It was a curious perspective peering up into the darkness of the interior of the ancient bell, since it was also a gaze into time.
When an old bell is recast, any inscriptions are copied onto the new one and an ancient bell like Great Tom may carry a collection of texts which reveal an elaborate history extending back through many centuries. The story of Great Tom begins in Westminster where, from the thirteenth century in the time of Henry III, the large bell in the clocktower of Westminster Palace was known as ‘Great Tom’ or ‘Westminster Tom.’
Great Tom bears an inscription that reads, ‘Tercius aptavit me rex Edwardque vocavit Sancti decore Edwardi signantur ut horae,’ which translates as ‘King Edward III made and named me so that by the grace of St Edward the hours may be marked.’ This inscription is confirmed by John Stowe writing in 1598, ‘He (Edward III) also built to the use of this chapel (though out of the palace court), some distance west, in the little Sanctuary, a strong clochard of stone and timber, covered with lead, and placed therein three great bells, since usually rung at coronations, triumphs, funerals of princes and their obits.’
With the arrival of mechanical clocks, the bell tower in Westminster became redundant and, when it was pulled down in 1698, Great Tom was sold to St Paul’s Cathedral for £385 17s. 6d. Unfortunately, while it was being transported the bell fell off the cart at Temple Bar and cracked. So it was cast by Philip Wightman, adding the inscription ‘MADE BY PHILIP WIGHTMAN 1708. BROUGHT FROM THE RVINES OF WESTMINSTER.’
Yet this recasting was unsatisfactory and the next year Great Tom was cast again by Richard Phelps at the Whitechapel Bell Foundry. This was also unsuccessful and, seven years later, it was was cast yet again by Richard Phelps at Whitechapel, adding the inscription ‘RICHARD PHELPS MADE ME 1716’ and arriving at the fine tone we hear today.
As well as chiming the hours at St Paul’s, Great Tom is also sounded upon the death of royalty and prominent members of the clergy, tolling last for the death of the Queen Mother in 2002. For the sake of my eardrums, I timed my visit to Great Tom between the hours. Once I had climbed down again safely to the ground, I walked around the west front of the cathedral just in time to hear Great Tom strike noontide. Its deep sonorous reverberation contains echoes of all the bells that Great Tom once was, striking the hours and marking out time in London through eight centuries.


Above the nave


Looking west with St Brides in the distance

Spare clock hands

Looking east along the roof of the cathedral

Up to the clock room

The bell frame for Great Paul in the clock room

Great Paul

Looking up to Great Paul

Looking across to the north west tower from the clock room



Looking south to the river

Looking across to the north west tower

Looking down on Great Paul

Looking up into the bell frame

Looking up to catch a glimpse of Great Tom, St Paul’s largest working bell

Great Tom cast by Richard Phelps in Whitechapel in 1716, engraved in 1776 (Courtesy of The Ancient Society of College Youths)

Great Tom strikes noon at St Paul’s Cathedral
You may also like to read about
The Secrets Of Christ Church
Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
There is a such a pleasing geometry to the architecture of Nicholas Hawksmoor’s Christ Church, Spitalfields, completed in 1729, that when you glance upon the satisfying order of the facade you might assume that the internal structure is equally apparent. Yet it is a labyrinth inside. Like a theatre, the building presents a harmonious picture from the centre of the stalls, yet possesses innumerable unseen passages and rooms, backstage.
Beyond the bellringers’ loft, a narrow staircase spirals further into the thickness of the stone spire. As you ascend the worn stone steps within the thickness of the wall, the walls get blacker and the stairs get narrower and the ceiling gets lower. By the time you reach the top, you are stooping as you climb and the giddiness of walking in circles permits the illusion that, as much as you are ascending into the sky, you might equally be descending into the earth. There is a sense that you are beyond the compass of your experience, entering indeterminate space.
No-one has much cause to come up here and, when we reached the door at the top of the stairs, the verger was unsure of his keys. As I recovered my breath from the climb, while he tried each key in turn upon the ring until he was successful, I listened to the dignified tick coming from the other side of the door. When he opened the door, I discovered it was the sound of the lonely clock that has measured out time in Spitalfields since 1836 from the square room with an octagonal roof beneath the pinnacle of the spire. Lit only by diffuse daylight from the four clock faces, the renovations that have brightened up the rest of the church do not register here.
Once we were inside, the verger opened the glazed case containing the gleaming brass wheels of the mechanism, turning with inscrutable purpose within their green-painted steel cage, driving another mechanism in a box up above that rotates the axles, turning the hands upon each of the clock faces. Not a place for human occupation, it was a room dedicated to time and, as intervention is required only rarely here, we left the clock to run its course in splendid indifference.
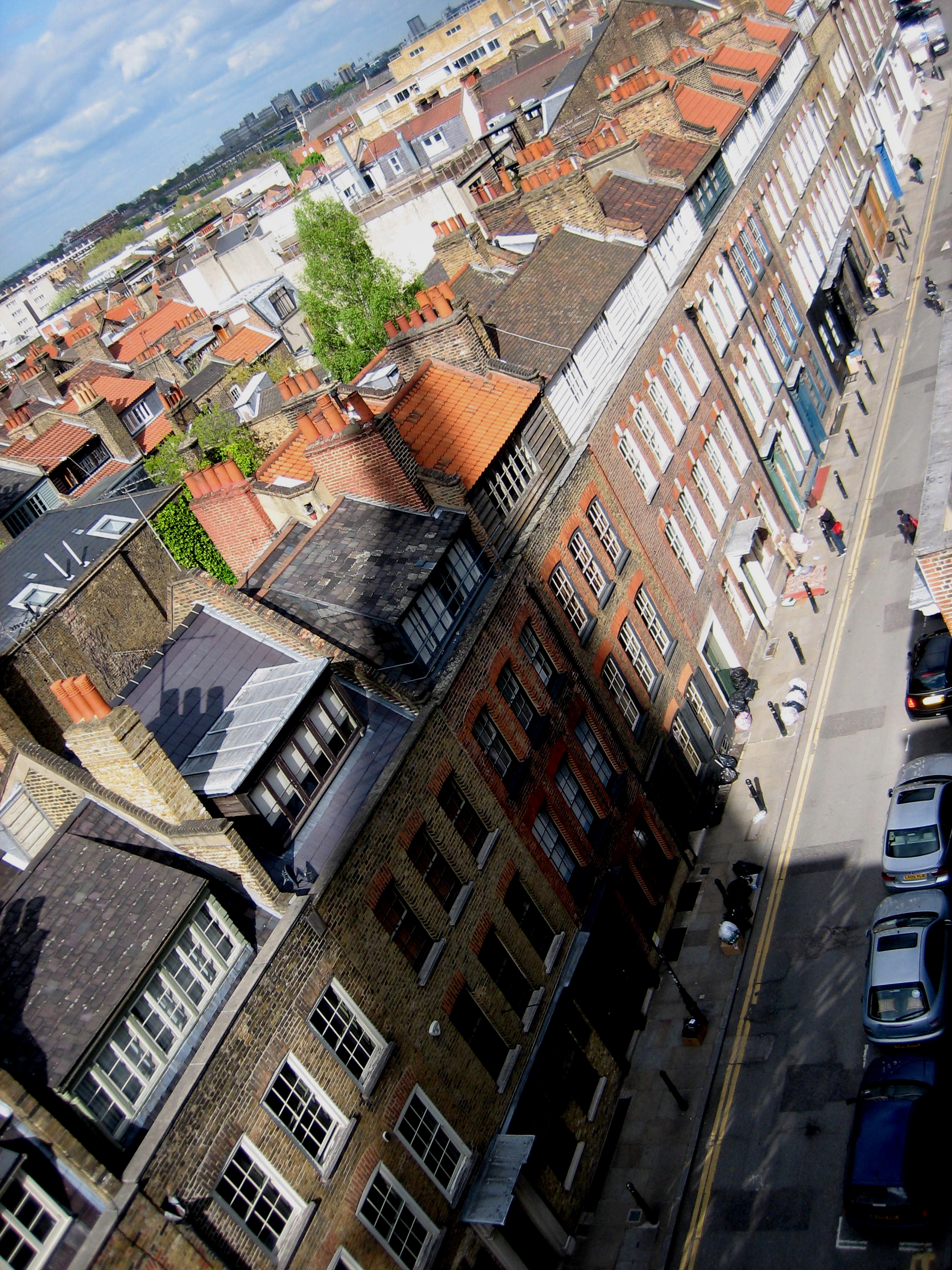
By contrast, a walk along the ridge of the roof of Christ Church, Spitalfields, presented a chaotic and exhilarating symphony of sensations, buffered by gusts of wind beneath a fast-moving sky that delivered effects of light changing every moment. It was like walking in the sky. On the one hand, Fashion St and on the other Fournier St, where the roofs of the eighteenth century houses topped off with weavers’ lofts create an extravagant roofscape of old tiles and chimney pots at odd angles. Liberated by the experience, I waved across the chasm of the street to residents of Fournier St in their rooftop gardens opposite, just like waving to people from a train.
Returning to the body of the church, we explored a suite of hidden vestry rooms behind the altar, magnificently proportioned apartments to encourage lofty thoughts, with views into the well-kept rectory garden. From here, we descended into the crypt constructed of brick vaults to enter the cavernous spaces that until recent years were stacked with human remains. Today these are innocent, newly-renovated spaces without any tangible presence to recall the thousands who were laid to rest here until it was packed to capacity and closed for burial in 1812 by Rev William Stond MA, as confirmed by a finely lettered stone plaque.
Passing through the building, up staircases, through passages and in each of the different spaces from top to bottom, there were so many of these plaques of different designs in wood and stone, recording those were buried here, those who were priests, vergers, benefactors, builders and those who rang the bells. In parallel with these demonstrative memorials, I noticed marks in hidden corners, modest handwritten initials, dates and scrawls, many too worn or indistinct to decipher. Everywhere I walked, so many people had been there before me, and the crypt and vaults were where they ended up.
My visit started at the top and I descended through the structure until I came, at the end of the afternoon, to the small private vaults constructed in two storeys beneath the porch, where my journey ended, as it did in a larger sense for the original occupants. These delicate brick vaults, barely three feet high and arranged in a crisscross design, were the private vaults of those who sought consolation in keeping the family together even after death. All cleaned out now, with modern cables and pipes running through, I crawled into the maze of tunnels and ran my hand upon the vault just above my head. This was the grave where no daylight or sunshine entered, and it was not a place to linger on a bright afternoon in August.
Christ Church gave me a journey through many emotions, and it fascinates me that this architecture can produce so many diverse spaces within one building and that these spaces can each reflect such varied aspects of the human experience, all within a classical structure that delights the senses through the harmonious unity of its form.
The mechanism of this clock runs so efficiently that it only has to be wound a couple of times each year
Looking up inside the spire
A model of the rectory in Fournier St
On the reverse of the door of the organ cupboard
In the vestry
For nearly three centuries, the shadow of the spire has travelled the length of Fournier St each afternoon
You may also like to read about
Glenys Bristow In Spitalfields
Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
Glenys with her dad Stanley Arnabaldi in their cafe at 100 Commercial St
When I met Glenys Bristow (1922-2017), she did not live in Spitalfields anymore but in a well-kept flat in a quiet corner of Bethnal Green. Glenys might never even have come to Spitalfields if the Germans had not dropped a bomb on her father’s cafe in Mansell St, down below Aldgate. In fact, Glenys would have preferred to stay in Westcliff-on-Sea and never come to London at all, if she had been given the choice. Yet circumstances prevailed to bring Glenys to Spitalfields. And, as you can see from this picture taken in 1943 – in the cafe she ran with her father opposite the market – Glenys embraced her life in Spitalfields wholeheartedly.
“I came to London from Westcliff-on-Sea when I was fifteen. I didn’t like London at all. At first we were in Limehouse, I walked over to Salmon Lane and there was Oswald Mosley making a speech to his blackshirts. The police told us to go home. I was sixteen and I missed Westcliff so, me and my friend, we took a job in a cafe there for the Summer. We were naive. We weren’t streetwise. We didn’t have confidence like kids do today.
The family moved to Mansell St where had a cafe – our first cafe – and we lived above it. My father’s name was Arnabaldi, I used to hate it when I was at school. My father always wanted to have a cafe of his own. His father had come over from Italy and ran a shop in Friern Barnet but died when my father was only eleven, and my father told me his mother died young of a broken heart.
In September 1940, we were bombed out of Mansell St. Luckily no-one was inside at the time because it was the weekend. It was a big shock. My mother, sister Rita and brother Raymond had gone to Wales to visit my grandparents in the Rhonda Valley. I’d left that afternoon with my husband Jack, who was my boyfriend then. We had something to eat at his sister’s then we went by bus to my future in laws at Old St, where we slept in an Anderson shelter. On Monday morning, we were walking back to Mansell St and these people asked, “Where are you going?” I said, “Home, I’m going to change before going to work.” “You’ll be lucky,” they said. When we got there we found the site roped off. It was all gone. Just a pile of rubble.”
Glenys got married at eighteen years old at Arbour Sq Registry Office when Jack was enlisted.”We didn’t know if we were going to be here from one day to the next,”she told me, describing her experience of living through the blitz, suffering the destruction of her home in the bombing and then finding herself alone with a baby while her husband was at war.
“In late 1942, my father got the cafe at 100 Commercial St, Spitalfields, and I was living in a little house in Vallance Rd and had my first baby John and he was just eleven months old. My father bought the cafe and he arranged for me to stay in the top floor flat next door at 102, Commercial St. We just had two rooms above some offices with a cooker on the landing and a toilet. When the air raid sirens went, I didn’t want to get out of bed so my dad fixed up a bell on a string from next door. I used to wrap my baby in an eiderdown and wait until the shrapnel had stopped flying before I went out of the door into the street to the cafe next door.
I did a bit of everything, cooking, serving behind the counter. People came in from the Godfrey & Phillips cigarette factory, the market and all the workshops. The fruit & vegetable market kept going all through the war but, because of the blackout, it started later in the night. We were lucky being close to the market, we were never short of anything.
At the end of the war, Jack came back and worked for my parents until, after a few years, the lease on the cafe ran out and we had to give it up. In 1956, we rented a little cafe in Hanbury St that belonged to the Truman Brewery, but we were only there three years before we had to move again because they had expansion plans. We bought the cafe opposite where Bud Flanagan had been born and called it Jack’s Cafe. And we were there from 1960 until 1971.
Because of the market, we had to have dinner ready to serve at nine in the morning, and again from twelve ’til two. Nothing was frozen, everything was cooked daily and Jack used to buy everything fresh from the market. They said we had the best and the cleanest cafe in the Spitalfields Market, and a lot of our customers became friends. My daughter met her husband there, he was a porter – his whole family were porters – and my son went to work as a porter, he was called an empty boy until he got his badge.
I just took it for granted. We used to open at half past four in the morning and I used to try and get cleaned up by half past six at night. It was very hard. Eventually, we sold it because I had back trouble and my husband bought a couple of lorries. In 1976, we moved from Commercial St to Chicksand St. I had four children altogether, only three that lived.
When it all changed, we went back – my daughter and I – to visit our old cafe. It had the same formica on the wall my husband had put up and I kept trying to look in the kitchen. I loved it when we worked for my mum and dad, and when we had our own place. I loved it and I miss it. They said I was the best pastry cook in Spitalfields.”
Glenys Bristow was a woman of astonishing resilience, possessing quick wits and a bright intelligence. Random events delivered her to Spitalfields in wartime, where she found herself at the centre of a lively working community. Losing everything when the bomb fell on her father’s cafe, and living day-to-day in peril of her life, she summoned extraordinary strength of character, bringing up her family and working long hours too. Glenys had no idea that she would live into another century, and enjoy the advantage of living peacefully in Bethnal Green and be able to look back on it all with affection.
Glenys Bristow (1922-2017)
Glenys’ home in Mansell St after the bomb dropped in 1940.
At the cafe in Mansell St.
Glenys and her daughter Linda, 1950
Glenys and Linda visit the site of the former cafe in Mansell St, 1951.
Glenys with her children, John, Linda and Alan.
Glenys and her husband Jack with their first car.
Stan, Jack, Glenys and her mother Anne on a day trip to Broxbourne.
Glenys’ identity card with Commercial Rd mistakenly substituted for Commercial St.
Glenys with her granddaughter Sue Bristow.
You may also like to read about
Sebastian Harding’s Architectural Models

Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October

Part of Sebastian Harding’s model of the Truman Brewery
Sebastian Harding‘s model of the Truman Brewery was the centrepiece of the Save Brick Lane exhibition, but he has been making architectural models for years – especially of buildings that are lost – and here are some of my favourites.
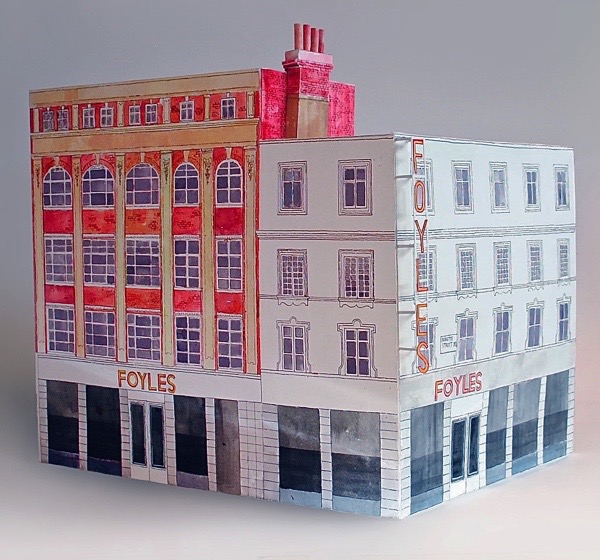

Foyles Building, 113-119 Charing Cross Rd
In 1929 William Foyles opened his newly expanded bookshop here after trading on the same street since 1906 and it soon became known as one of the largest of its kind in Europe.
The Charing Cross Rd facade dates from the early nineteen-hundreds and boasts a simple asymmetric design built of plum red brick with classical columns. The building ran back the length of Manette St with a bolder Art Deco facade dating from 1929 and these two facades were charmingly interrupted on the corner of the building by an early Victorian stuccoed facade.
For generations of book lovers, this huge building provided a haven of tranquility in the noisy and chaotic hub of central London. For over eighty years Foyles, with its labyrinthine layout, sprawling floors and large cafe was far more than just a bookshop. Full of oddly-shaped spaces and quiet corners, the place exuded an irresistibly-inviting atmosphere.

The Marquis of Lansdowne, Cremer St, Hoxton
Opening before 1838, The Marquis of Lansdowne was a typical East End pub which became the focus for workers in the cabinet-making trades which filled the surrounding streets for over a century. After drastic slum clearance and redevelopment in Hoxton in the mid-twentieth century, the pub fell into decline and closed. In 2013 David Dewing, Director of the Geffrye Museum (now the Museum of the Home) announced the demolition of the pub for the sake of a concrete cube restaurant as part of a multi-million pound revelopment of the museum designed by Sir David Chipperfield. However, largely thanks to a campaign by readers of Spitalfields Life, Hackney Council refused permission for demolition of the historic pub. Subsequently, the Heritage Lottery Fund supported a new scheme by Wright & Wright which requires no demolition, expanding the museum’s galleries by opening up unused spaces in the existing buildings and restores the Marquis of Lansdowne.
The Saracen’s Head, 4-7 Aldgate High St
The Saracen’s Head public house was demolished in 1913. Even in the late nineteenth century, Aldgate survived as a slice of sixteenth and seventeenth century London until the developers moved in from the eighteen eighties to modernise these streets. It was one of the few places to avoid the Great Fire of 1666, where the locals gathered to watch the conflagration. This makes the Saracen’s Head all the more important to the area’s history and, though long gone, there is a plaque at No. 88 Aldgate High St commemorating its existence.
It operated as a coaching inn with a service that departed from the yard at the back, transporting Londoners to East Anglia – hence the building’s location on the main road eastward out of the city. The frontage holds wonderful early examples of Baroque decoration and the ornate moulding echoes the decoration seen on the Baroque post-Fire churches – including St Paul’s – that emerged throughout London at the time. When the building was demolished, it was functioning as the Metropole Restaurant with the Ladies Select Dining Room housed on the first floor. After its destruction, the Guildhall Museum bought the intricate wooden pilaster capitals for their collection, confirming its aesthetic importance.
Nicholas Culpeper’s House, Red Lion Field, Spitalfields
In 1640, when Nicholas Culpeper, the herbalist, married Alice Field, aged fifteen, he was able to build a substantial wooden house in Red Lion Field, Spitalfields, with her dowry. Here, he conducted his practice, treating as many as forty citizens in a morning, and in the land attached he cultivated herbs – collecting those growing wild in the fields beyond. Since Culpeper never finished his apprenticeship, he could not practise in the City of London but chose instead to offer free healthcare to the citizens of Spitalfields, much to the ire of the Royal College of Physicians. In this house, Nicholas Culpeper wrote his masterwork known as Culpeper’s Herbal which is still in print today.
After Culpeper’s death, the building became the Red Lion public house, surviving into the nineteenth century when it was demolished, as part of the road widening for the creation of Commercial St to carry traffic from the London Docks.
186 & 184 Fleet St
If you were to take a stroll down Fleet St today, you might like to take a closer look at the buildings that stand at 186 & 184. They perch immediately to the right of St-Dunstan-in-the-West on the north side of the Street in a row of inconspicuous turn-of-the-century buildings. On closer inspection each appears distinct, but all three are somewhat tall and somewhat narrow. Their cramped proportions are explained by the fact they were built, like much of London, on the site of two ancient pre-fire buildings.
The history of the nineteenth century buildings that occupy the site today relates directly to the rise of the newspaper trade that proliferated in the area. Indeed, Fleet St is still synonymous with British journalism despite all major publications now being headquartered elsewhere.
Today the site of 184 & 186 is home to the Scottish firm D.C. Thomson & Co., who claim to be the last newspaper group to retain a base on Fleet St, and the titles of their publications, The Sunday Post and The Dundee Courier, are still proclaimed in mosaic on the façade of their neighbour at 188.
Part of Rothschild Buildings, Spitalfields
Before their demolition in the seventies, the Rothschild Dwellings were visited by historian Jerry White whose first impression of the buildings was that he had “never seen tenements, so starkly repulsive” and “so much without one redeeming feature” in his whole life.
The Rothschild Dwellings were erected in 1888 by the ‘Four percent Industrial Dwellings Company’ and stood on the sight of what had once been respectable middle class residences in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, which had degenerated into lodging houses and slums. In the mid-nineteenth century, the old filthy streets with their myriad alleyways and courts were swept away. In their place, came the wide thoroughfare of Commercial St and large housing blocks such as the Nathaniel Dwellings (1892), the Lolesworth Buildings (1885) and, of course, the Charlotte De Rothschild Dwellings (1887). The tenants of these buildings were respectable working class tradesmen and craft workers able to pay the slightly higher rent.
The Fortunes Of War Public Tavern, Cock Lane, Smithfield
Smithfield Market’s proximity to St Bartholomew’s Hospital betrays a lot about the British public’s distrust of the medical trade. It is fitting therefore to focus on one building that catered to both trades – The Fortunes Of War Public Tavern.
Let us place ourselves in the eighteenth century as we watch a student of anatomy making his way into the tavern. He is here, not as you would expect for his leisure, but for his studies. He is led by the landlord down dank mouldering stairs to the cellar. Rows of sacks give off a pungent smell of rotting meat, yet these are not the carcasses of swine or cattle but the bodies of recently dead Smithfield residents.
This was the secret trade of the Body Snatchers or Resurrectionists that supplied students and professors of anatomy with fresh corpses. For a God-fearing public, it was immoral and barbarous in the extreme, for this was a time when many believed a soul would only be granted into heaven if their corporeal body was intact, while being dissected meant an eternity in purgatory.
John Aston’s House, Charterhouse Lane
John Aston was a priest in the parish of Smithfield, arrested at the same time as the influential protestant leader John Rogers. Queen Mary’s secret police randomly inspected any priests who had been advocates of protestantism before her ascension to the throne in 1553.
Unsurprisingly, the inspections would usually find a protestant bible or a mass being held. Typically, the raids were held on Sundays and John Aston’s misfortune was to be found eating meat in one of these raids. The tyrannical catholic religion of the sixteenth century forbade any consumption of meat on Sunday and he was burnt at the stake for this trifling pretence.
20 Cock Lane, Smithfield
The name of this street can be traced to its proximity to the market, where poultry would once have been traded, but it also serves also as a risqué innuendo, since for hundreds of years it was the preferred haunt of prostitutes. It was on this street that fraud, haunting, murder and sex were all intertwined in one story.
Late one November night in 1760,William Kent was away on business in Norfolk. His wife Fanny, wishing to alleviate the loneliness of her nights alone, invited Betty the youngest daughter of the Parsons – the landlord’s family – to sleep in her bed. In the night, Fanny was disturbed by scratching sounds like claws on wood and lay frozen with fear. On appealing to Mr & Mrs Parsons, she was told a shoemaker lived next door and her fears were assuaged. But the next night was Sunday when no good Christian would ever work, yet the scratching came again, brought to a terrifying end by a loud bang.
After William Kent returned the next night the sounds were not heard again. Then, two months’ later, after a furious row, Mr Parsons threw the Kents’ possessions out onto the street, even though William had not received a penny of the money he had loaned to his landlord the previous year. Subsequently, Fanny succumbed to smallpox and died on February 2nd 1761.
Some time later, the Parsons family began to hear the same scratching again and made sure it became a talking point for superstitious members of the community. The methodist preacher John Moore held a séance and ,when he asked if a spirit was present, a knock rang out. A second question followed – “Was the spirit that of the late Fanny?” Another knock. “Was Fanny murdered by her husband?” the reverend asked and then followed the loudest banging the party had heard.
Subsequently, William Kent was hanged, but afterwards the events were revealed as a fraud motivated by the feud between Mr Parsons and his tenant over the loan. Parsons was sentenced to three years in prison and three days in pillory, but later became regarded as something of a celebrity.
Mother Clapp’s Molly House, Field Lane
This was not a coffee house as we would know it, but rather a private club for gay gentlemen, where they could meet and form relationships without fear of discovery. The discretion of fellow members was crucial and entry was only permitted to those who knew a password. There were even gay marriage ceremonies conducted in locked rooms between men, with one donning a bride’s dress and the other a groom’s jacket. Mother Clapp herself presided over all, only leaving to get refreshments from the pub across the street.
Everything we know about this secret sub-culture stems from the raid by The Society For The Reformation Of Manners which had placed secret police inside the house. One man, a milkman, was hung for being found in the act of sodomy and Mother Clapp was sentenced to a day in the pillory. The crowd was so furious that they ripped the pillory from the ground and trampled it, and Mother Clapp died from the injuries sustained.
Sebastian Harding
Illustrations copyright © Sebastian Harding
You may also like to read about
The Signs Of Old London

Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
The little wooden midshipman outside Solomon Gillis’ chandlery, 157 Leadenhall St
Even though most of the signs of old London were destroyed in the Great Fire of 1666, a few created just after that date survive today in the City – anachronisms affixed to modern buildings, as if they were Penny Blacks stuck onto Jiffy padded envelopes. Yet in the Bishopsgate Institute archive, I found plenty of atmospheric pictures of curious stone plaques which lasted into the era of photography, only to be destroyed by the blitz and subsequent redevelopment.
It was Charles I who gave people the right to hang out signs as they pleased, when once they were restricted to innkeepers – “for the better finding out such citizens’ dwellings, shops, pubs or occupations, without impediment, molestation, or interruption to their heirs or successors.” An elaborate language of symbols quickly grew in the common understanding, such as a dragon for an apothecary, a sugar loaf for a grocer, a wheatsheaf for a baker, a frying pan for a confectioner, and – as still seen in Spitalfields today – a spool for a silk weaver.
As time went by, the meanings of the signs became more complex and arcane as shops changed ownership but retained the signs as identifiers of the buildings. James Maddox, the coffin maker at St Olaves had the symbol of three coffins and a sugarloaf, the sugarloaf because it was a former grocers and three coffins as his personal device. Opposite St Dunstan’s in Fleet St, a sign of three squirrels first put up by Henry Pinkley the goldsmith in 1649, was appropriated by the bankers who moved in afterwards, and this symbol of the three squirrels continued to be used by the National Westminster Bank until the mid-twentieth century.
Lombard St was once famed for its array of magnificent signs, and eighteenth century prints show quaint symbols hung upon elaborate wrought iron brackets outside every single premises in Cornhill and Cheapside. Anticipating our modern concern with brands and logos, these devices suited the city before streets were numbered and when many of the populace did not read. But during heavy weather and in strong wind, these monstrous signs creaked and groaned – and, in 1718, a huge sign in Bride St collapsed killing four people and taking part of the shop front with it. Such was the severity of the problem of the forest of hanging signs crowding the streets of London, that a commission was appointed in 1762 to take them all down and fix them onto the shopfronts – thereby creating the modern notion of the fascia sign declaring the identity of the premises.
“The Commissioners are empowered to take down and remove all signs and emblems, used to denote the trade, occupation or calling – any sign posts, sign boards, sign irons, balconies, penthouses, show boards, spouts and gutters projecting into the streets etc, and all other encroachments and projections whatsoever in the said cities and liberties – and cause the same, or such parts thereof as they think fit to be affixed or placed on the front of the houses, shops, alehouses or buildings to which they belong.”
Street numbers were only in partial use at the beginning of the eighteenth century, becoming widespread by the end of the century as a standardised system to identify properties. Although many were reluctant to give up the language of signs and symbols, by the middle of the nineteenth century, the signs were commonly replaced by the familiar pattern of a board with signwriting above the shopwindow. Most of the decorative signs to found in the City of London today are pastiches created a hundred years ago as nostalgic tributes to a bygone age, though two favourites of mine are the golden owl on the House of Fraser, facing South over London Bridge, and the figure of Atlas holding up the globe on the exterior of Barclays in Cheapside.
Just three signs remain in common usage, the barbers’ pole (with its bloody red and white stripe recalling when barbers were also surgeons), the chemists’ pestle and mortar, and the pawnbrokers’ three balls – originally blue, they turned gold in the early nineteenth century and are said to be based upon the crest of the Dukes of Medici, itself derived from coins taken by Crusaders from Byzantium.
At the sign of the Fox in Lombard St.
At the sign of the Three Kings in Lombard St.
At the sign of the Half Moon in Holywell St, off the Strand.
A physician.
A locksmith.
At the sign of the Lamb & Flag
The grasshopper, symbol of industry and personal emblem of Sir Thomas Gresham who founded the Royal Exchange, is to be found all over the City of London even today.
At the sign of Three Squirrels in Fleet St.
At the sign of the Bull & Mouth in Aldgate.
This was the symbol of the Cutlers.
Child’s bank at the sign of the Marigold in Temple Bar.
In Ely Place, off Hatton Garden – this mitre came from an episcopal palace and was set into the wall of a public house.
The maid of the Mercer’s company is still to be seen in Corbet Court off Gracechurch St.
An old sign that remains in situ outside St Paul’s tube station.“When ye have sought the Citty round, yet still this is the highest ground. August 27th 1698”
“- an old sign affixed to a modern building, like a Penny Black stuck onto a Jiffy padded envelope.”
Photographs courtesy Bishopsgate Institute
Parkash Kaur, Shopkeeper

Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
‘We Punjabi girls are strong.’
Contributing Photographer Sarah Ainslie & I first met Parkash Kaur when we were making portraits of the residents of the Holland Estate next to Petticoat Lane in Spitalfields. It was evident then that Parkash occupied a revered position among the residents as spiritual mother to the entire estate.
Only when I was working with Suresh Singh on his memoir, A MODEST LIVING, did I discover that Parkash was a Sikh who famously ran a grocers shop at 5 Artillery Passage with her husband Jarnail Singh. So close were these two Sikh families in Spitalfields that Suresh and his wife Jagir know Parkash as Aunty Ji and, in Suresh’s childhood, he knew Jarnail as Uncle Jarnail.
Jarnail came to London in 1951 from Jundalar in the Punjab to seek a better life and his wife Parkash joined him in 1953. They had been married when they were children. By 1958, they had saved enough money to put a deposit on a shop in Artillery Passage and in 1963 they bought it and moved in, opening the first Sikh grocer in East London.
Around 2000, they closed their shop and retired to live fifty yards away in the Holland Estate. Since Jarnail died in 2010, Parkash lives alone but Suresh & Jagir visit her regularly. Sarah Ainslie & I accompanied them recently and we shared a delicious dinner of Jagir’s homemade rotis and yoghurt while Parkash told her story to Suresh, who has translated it from Punjabi for us to read.
“Your father and my husband made a pact of love and they called themselves the ‘rodda’ Sikhs (the ones without turbans). They had this silent love that they kept dear between them and always knew of each other’s joy and pain, sometimes even without talking.
They sat and talked all day long in our shop at 5 Artillery Passage where me and your Uncle worked day and night. I would shut the heavy shutters in the evening and sleep on the top floor while your Uncle went to do a night shift at the rubber factory in Southall. I walked back the other day to Artillery Passage and I could not even find the door or the number. No one there spoke Hindi or Punjabi any more and I felt a deep loss. It made me very sad.
Our days started at 4am each morning when your Uncle Jarnail would bring boxes of fruit and vegetables from the Spitalfields Market across the road. Big rats would jump out of some of the boxes. I was so scared of the rats, but we had a lovely niece working for us who could catch them by their tails. She would never kill them, but lift the heavy grate from the sewer and send them back. She said they where gods.
Suresh, this was when you were very little. I remember your mother Chinee would always wave and call out ‘Sat Shri Akal’ (blessings to all) to me from far away, if she saw me in Petticoat Lane or in Itcy Park next to the big white church. She was a very observant women who always stuck by your father, Joginder.
I was so happy when your parents invited me and your Uncle Jarnail to your wedding with Jagir in 1984. It was a joyful occasion for Joginder. After his stroke, your father struggled to walk yet he would always come every day from Princelet St to our shop in Artillery Passage and ask your Uncle Jarnail, ‘Do you think we have enough roti flour?’ For a long time, we were the only shop in East London that sold roti flour and people would come from as far away as Mile End and Plaistow.
Your Uncle Jarnail and Joginder helped each other with money, they never wanted to let each other down. People would say ‘Jarnail is a jatt (a farm owner) but Joginder is a chamar (an untouchable).’ Your uncle would reply, ‘Get out of my shop! We do not believe in castes here. He is my brother.’
All the money earned by Punjabis in East London passed through our shop and we sent it over to the Punjab and exchanged it for rupees, so people could build big houses over there. Once I sat on thousands of pounds in cash all on my own while your Uncle was out, before it was sent to the Punjab. I learnt to be a very good counter of money. In those days, people were naive enough to believe that one day they would all take their families back to the Punjab and live there for ever. But in Joginder’s eyes, he knew the truth.
He was happy to spend time with your Uncle Jarnail in the shop. They often spoke of the assassin Udam Singh who lodged in 15 Artillery Passage in the thirties. He shot Michael O’ Dwyer who ordered the massacre of Sikhs in Amritsar when he was Lieutenant Governor of the Punjab.
When me and your Uncle Jarnail needed a break from the hard work of shopkeeping, dealing with customers who never wanted to pay the asking price and always wanted to barter, we would sit on the wall outside Artillery Passage and eat ice cream from another shop – just to have a change. That was our holiday.
Where are all those people who came to our shop now? All gone. The ones that we helped out, where are they? Not to be seen. But you and Jagir are here with me and you know you are always welcome in my home. I am happy that you and Jagir and look after me. Your Uncle Jarnail died and left me alone but I am strong. We Punjabi girls are strong.”
Portraits by Sarah Ainslie
Parkash Kaur
Jarnail Singh
Jarnail ouside the grocery shop he ran with Parkash at 5 Artillery Passage
Parkash in her flat the Holland Estate (Photograph by Sarah Ainslie)
Jagir Kaur, Parkash Kaur & Suresh Singh (Photograph by Sarah Ainslie)

Suresh Singh & Jagir Kaur at 38 Princelet St last summer (Photograph by Patricia Niven)
You may also like to read about

Summer At Bow Cemetery

Book now for my tours of Spitalfields in August, September & October
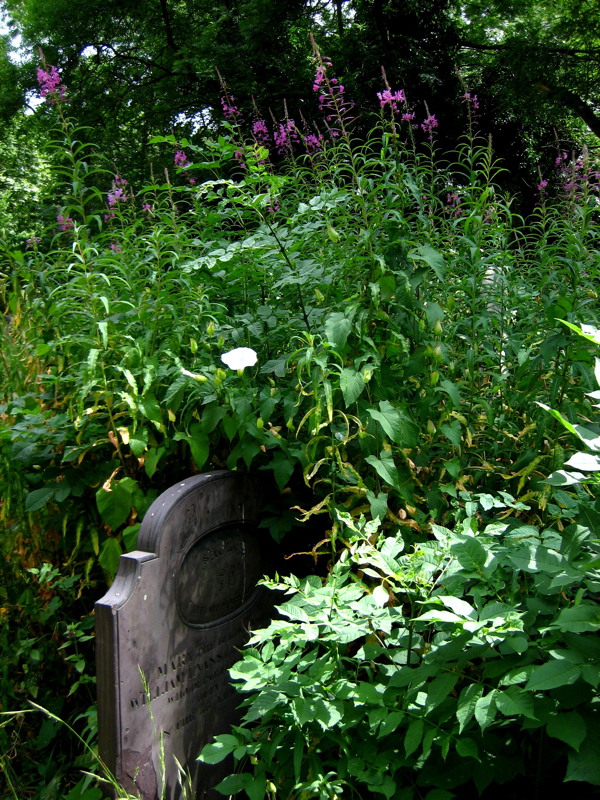

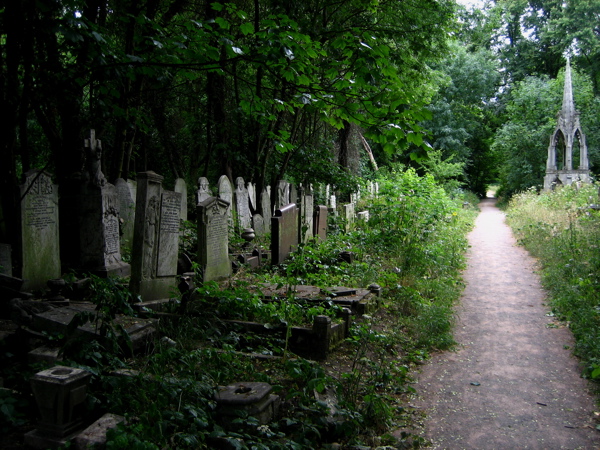
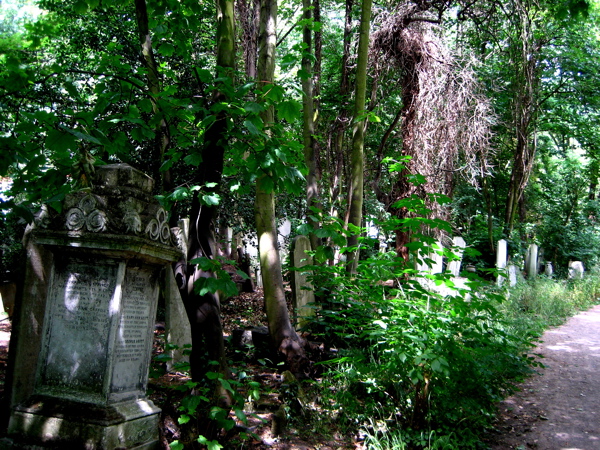
At least once each Summer, I direct my steps eastwards from Spitalfields along the Mile End Rd towards Bow Cemetery, one of the “Magnificent Seven” created by act of Parliament in 1832 as the growing population of London overcrowded the small parish churchyards. Extending to twenty-seven acres and planned on an industrial scale, “The City of London and Tower Hamlets Cemetery” as it was formally called, opened in 1841 and within the first half century alone around a quarter of a million were buried here.
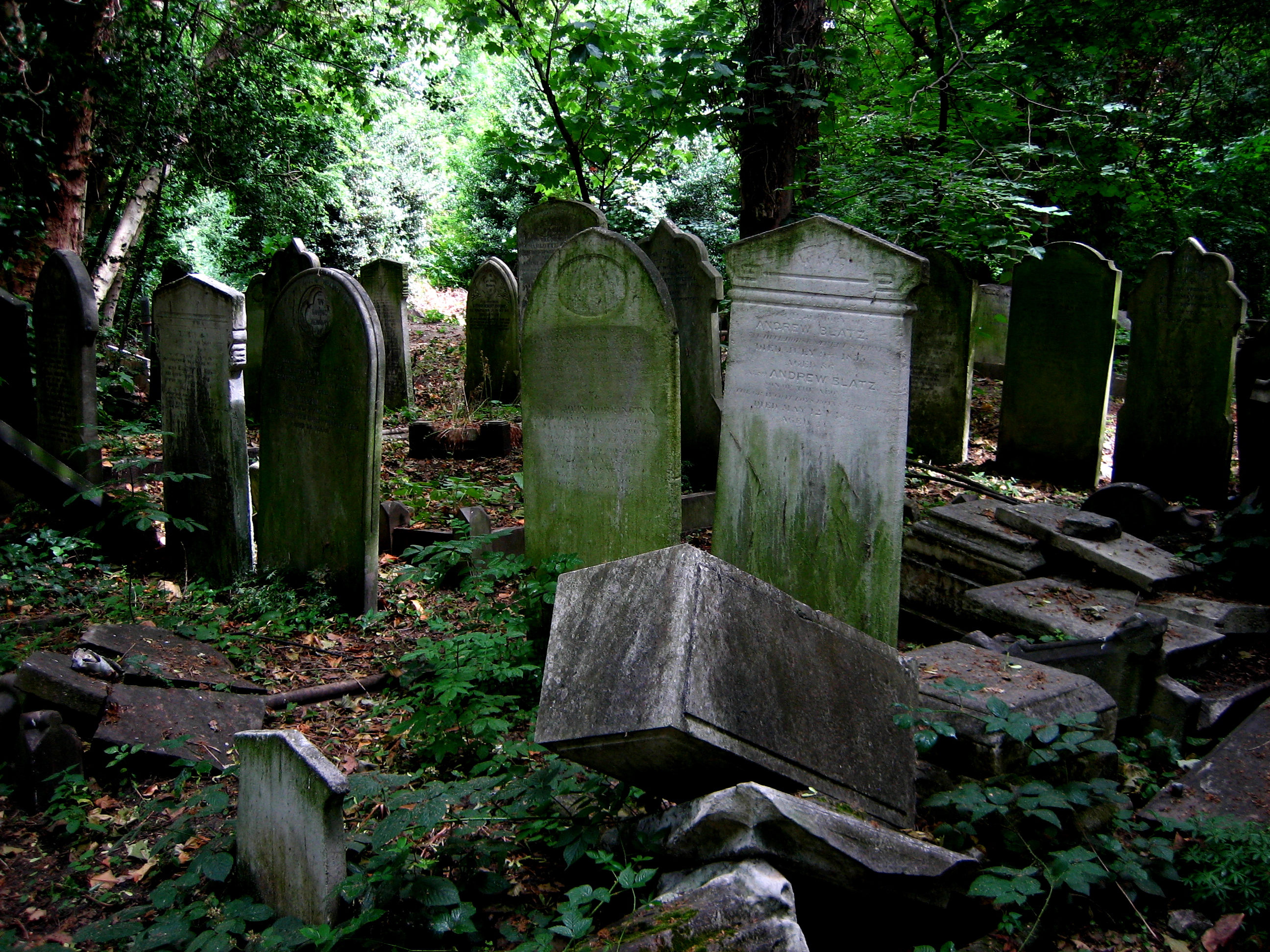
Although it is the tombstones and monuments that present a striking display today, most of the occupants of this cemetery were residents of the East End whose families could not afford a funeral or a plot. They were buried in mass public graves containing as many as forty bodies of random souls interred together for eternity. By the end of the nineteenth century the site was already overgrown, though burials continued until it was closed in 1966.
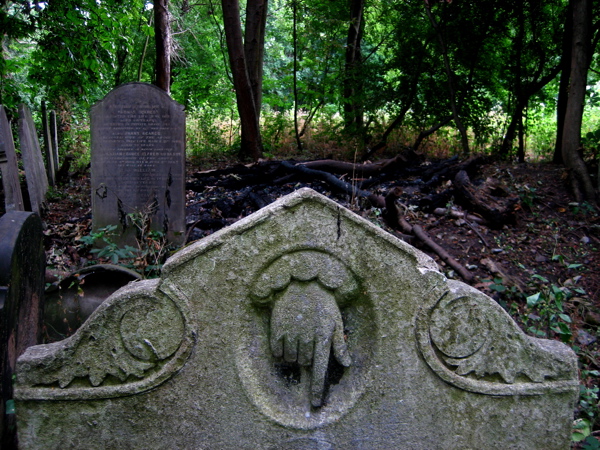
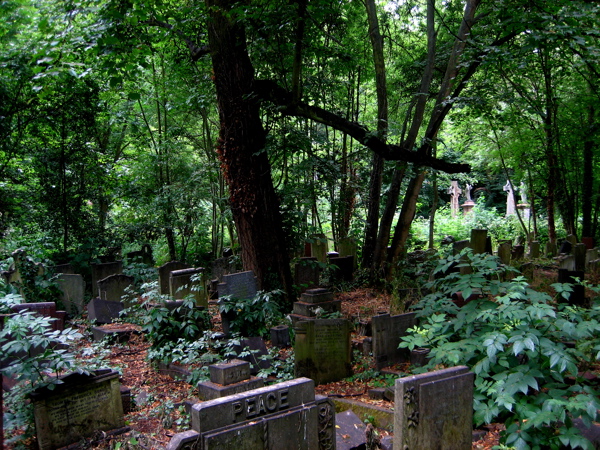
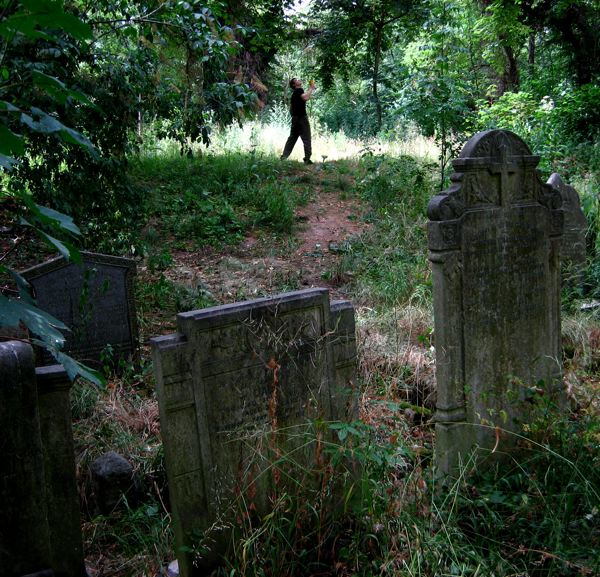
Where death once held dominion, nature has reclaimed the territory and a magnificent broadleaf forest has grown, bringing luxuriant growth that is alive with wildlife. Now the tombstones and monuments stand among leaf mould in deep woods, garlanded with ivy and surrounded by wildflowers. Tombstones and undergrowth make one of the most lyrical contrasts I can think of – there is a beautiful aesthetic manifest in the grim austerity of the stones ameliorated by vigorous plant life. But more than this, to see the symbols of death physically overwhelmed by extravagant new growth touches the human spirit. It is both humbling and uplifting at the same time. It is the triumph of life. Nature has returned and brought more than sixteen species of butterflies with her.
This is the emotive spectacle that leads me here, turning right at Mile End tube station and hurrying down Southern Grove, increasing my pace with rising expectation, until I walk through the cemetery gates and I am transported into the green world that awaits. At once, I turn right into Sanctuary Wood, stepping off the track to walk into a tall stand of ivy-clad sycamores, upon a carpet of leaves that is shaded by the forest canopy more than twenty metres overhead and illuminated by narrow shafts of sunlight descending. It is sublime. Come here to see the bluebells in Spring or the foxgloves in Summer. Come at any time of the year to find yourself in another landscape. Just like the forest in Richard Jefferies’ novel “After London,” the trees have regrown to remind us what this land was once like, long ago before our predecessors ever came here.
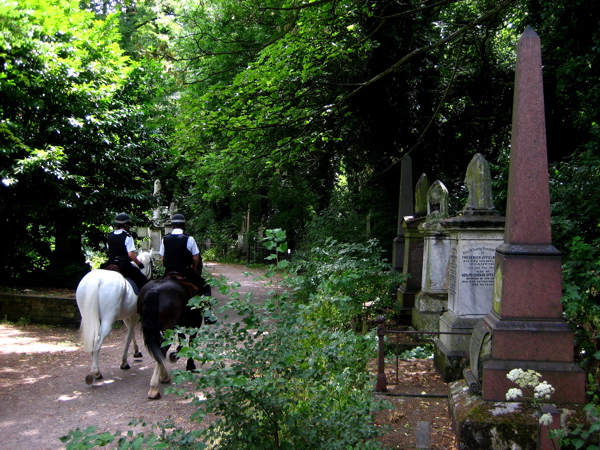
Over time, the tombstones have weathered and worn, and some have turned green, entirely harmonious with their overgrown environment, as if they sprouted and grew like toadstools. The natural stillness of the forest possesses greater resonance between cemetery walls and the deep green shadows of the woodland seem deeper too. There was almost no-one alive to be seen on the morning of my visit, apart from two police officers on horseback passing through, keeping the peace that is as deep as the grave.
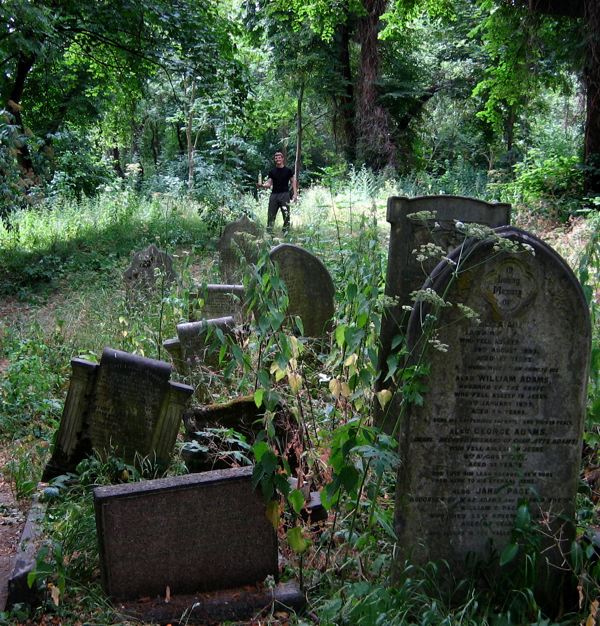
Just as time mediates grief and grants us perspective, nature also encompasses the dead, enfolding them all, as it has done here in a green forest. These are the people who made East London, who laid the roads, built the houses and created the foundations of the city we inhabit. The countless thousands who were here before us, walking the streets we know, attending the same schools, even living in some of the same houses we live in today. The majority of those people are here now in Bow Cemetery. As you walk around, names catch your eye, Cornelius aged just two years, or Eliza or Louise or Emma, or Caleb who enjoyed a happy life, all over a hundred years ago. None ever dreamed a forest would grow over their head, where people would come to walk one day to discover their stones in a woodland glade. It is a vision of paradise above, fulfilled within the confines of the cemetery itself.
As I made my progress through the forest of tombstones, I heard a mysterious noise, a click-clack echoing through the trees. Then I came upon a clearing at the very heart of the cemetery and discovered the origin of the sound. It was a solitary juggler practicing his art among the graves, in a patch of sunlight. There is no purpose to juggling than that of delight, the attunement of human reflexes to create a joyful effect. It was a startling image to discover, and seeing it here in the deep woods – where so many fellow Londoners are buried – made my heart leap. Outside on the streets, a million people were going about their business while in the vast wooded cemetery there was just me, the numberless dead and the juggler.











Find out more at Friends of Tower Hamlets Cemetery Park
You may also like to read about